Twelve-Week Colostrum Bovinum Supplementation Supports Aerobic Capacity but has No Effect on Body Composition in Endurance-Trained Males: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study
- PMID: 40254930
- PMCID: PMC12010043
- DOI: 10.1002/ejsc.12288
Twelve-Week Colostrum Bovinum Supplementation Supports Aerobic Capacity but has No Effect on Body Composition in Endurance-Trained Males: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study
Abstract
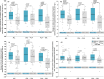
Twenty-eight endurance-trained males aged 31.1 ± 10.2 years (body mass [BM] 81.9 ± 9.0 kg) completed this randomized double-blind placebo (PLA)-controlled crossover study investigating the effect of 12-week Colostrum Bovinum (COL) supplementation (25gCOL·day-1) on aerobic fitness and capacity, time to exhaustion, BM and body composition (BC), and blood lactate concentration. There were four main-before/after supplementation study visits (COLPRE and COLPOST; PLAPRE, and PLAPOST). During study visits, BM and BC evaluation, incremental rowing test (IRT) to exhaustion, and evaluation of resting (REST) and post-exercise (POST-IRT) blood lactate concentration were performed. COL, but not PLA supplementation, significantly increased (p < 0.05) time to ventilatory threshold (TVT). Moreover, the implemented treatments had large (mL·min-1) and moderate (mL·min-1·kg-1) effects on oxygen uptake at VT (VO2VT), as well as moderate effect on power output at VT (PVT; W·kg-1) with the highest values observed at COLPOST visit. Neither significant influence of COL supplementation on time to exhaustion (TEXH) in IRT, BM, and BC on blood lactate was observed. Importantly, there were significantly (p < 0.05) higher increases in VO2VT (mL·min-1 and mL·min-1·kg-1) after COL compared to PLA supplementation. In summary, COL supplementation resulted in a favorable increase in TVT, and tended to improve some of the evaluated threshold indicators, namely VO2VT and PVT in endurance-trained male athletes during IRT. Therefore, COL supplementation may be considered as a support to improve aerobic fitness and capacity in endurance-trained males; however, supplementation strategy must be personalized and properly incorporated into the individual training. TRIAL REGISTRATION: The study protocol was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT06390670).
Keywords: ergogenic support; proteins; supplementation; swimming; triathlon.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Sport Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European College of Sport Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Does Colostrum Bovinum Supplementation Affect Swimming Performance in Endurance-Trained Males? A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Crossover Study.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 22;16(18):3204. doi: 10.3390/nu16183204. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339805 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of 12-week high-dose Colostrum Bovinum supplementation on immunological, hematological and biochemical markers in endurance athletes: a randomized crossover placebo-controlled study.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 21;15:1425785. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1425785. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39497827 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of a β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate supplementation on physical capacity, body composition and biochemical markers in elite rowers: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover study.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Jul 30;12:31. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0092-9. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26225130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Effect of β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate on Aerobic Capacity and Body Composition in Trained Athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2016 Sep;30(9):2617-26. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000001361. J Strength Cond Res. 2016. PMID: 26849784 Clinical Trial.
-
Protein supplementation increases adaptations to endurance training: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Nutr. 2021 May;40(5):3123-3132. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2020.12.012. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Clin Nutr. 2021. PMID: 33358231
References
-
- Brinkworth, G. D. , Buckley J. D., Bourdon P. C., Gulbin J. P., and David A. Z.. 2002a. “Oral Bovine Colostrum Supplementation Enhances Buffer Capacity but Not Rowing Performance in Elite Female Rowers.” International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism 12, no. 3: 349–363. 10.1123/ijsnem.12.3.349. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

