The Chain Mediating Effect of Health Literacy and Self-Care Ability on the Relationship Between Dysmenorrhea Symptoms and Negative Emotions Among Chinese Female College Students
- PMID: 40255274
- PMCID: PMC12009575
- DOI: 10.2147/IJWH.S511601
The Chain Mediating Effect of Health Literacy and Self-Care Ability on the Relationship Between Dysmenorrhea Symptoms and Negative Emotions Among Chinese Female College Students
Abstract
Background: Dysmenorrhea, a common concern among female college students, is closely linked to anxiety and depression, particularly during the early menstrual phase (the first one to two days of menstruation), when cramping pain in the lower abdomen and other discomforts occur. This study aims to assess the current status of dysmenorrhea and negative emotions among female college students and explore the factors influencing the relationship between menstrual pain and negative emotions.
Methods: A total of 1,117 female college students with moderate to severe dysmenorrhea (based on a Visual Analog Scale (VAS) ≥ 4) were recruited from five universities in Guangdong Province through purposive and convenience sampling to complete an online survey between August and October 2024. Data were collected using multiple standardized scales. Pearson correlation coefficients were used to examine the relationships between variables. Multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to analyze the effects of variables with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) identified through one-way ANOVA, independent sample t-tests, and correlation analysis on psychological levels. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was used to explore mediating effects.
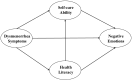
Results: This study shows that dysmenorrhea symptoms, health literacy, self-care ability, and negative emotions are significantly correlated. Health literacy and self-care ability play a chain mediating role between dysmenorrhea symptoms and negative emotions, with a mediating effect of 0.026, accounting for 4.87% of the total effect.
Conclusion: The findings suggests that health literacy and self-care ability play a chain-mediating role between dysmenorrhea symptoms and negative emotions. It provides new insights for intervening in emotional issues related to dysmenorrhea in female college students. Universities and healthcare institutions should focus on enhancing health literacy and self-care abilities among female college students, offering effective health education and resources to help them better manage menstrual pain and reduce anxiety and depression.
Keywords: dysmenorrhea symptoms; female college students; health literacy; negative emotions; self-care ability.
© 2025 Luo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources