Hidden β-γ Dehydrogenation Products in Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Unveiled by NMR: Implications on Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 40255280
- PMCID: PMC12006827
- DOI: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.4c00140
Hidden β-γ Dehydrogenation Products in Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Unveiled by NMR: Implications on Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
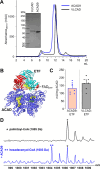
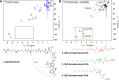
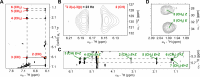
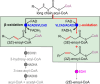
We present a comprehensive analysis of the initial α,β-dehydrogenation step in long-chain fatty acid β-oxidation (FAO). We focused on palmitoyl-CoA oxidized by two mitochondrial acyl-CoA dehydrogenases, very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLCAD) and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family member 9 (ACAD9), both implicated in mitochondrial diseases. By combining MS and NMR, we identified the (2E)-hexadecenoyl-CoA as the expected α-β-dehydrogenation product and also the E and Z stereoisomers of 3-hexadecenoyl-CoA: a "γ-oxidation" product. This finding reveals an alternative catalytic pathway in mitochondrial FAO, suggesting a potential regulatory role for ACAD9 and VLCAD during fatty acid metabolism.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Honda A.; Nozumi M.; Ito Y.; Natsume R.; Kawasaki A.; Nakatsu F.; Abe M.; Uchino H.; Matsushita N.; Ikeda K.; Arita M.; Sakimura K.; Igarashi M. Very-long-chain fatty acids are crucial to neuronal polarity by providing sphingolipids to lipid rafts. Cell Reports 2023, 42 (10), 113195.10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113195. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leslie N.; Wang X.; Peng Y.; Valencia C. A.; Khuchua Z.; Hata J.; Witte D.; Huang T.; Bove K. E. Neonatal multiorgan failure due to ACAD9 mutation and complex I deficiency with mitochondrial hyperplasia in liver, cardiac myocytes, skeletal muscle, and renal tubules. Human Pathology 2016, 49, 27–32. 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.09.039. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
