Clinical potential and experimental validation of prognostic genes in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by risk modeling utilizing single cell and transcriptome constructs
- PMID: 40255404
- PMCID: PMC12006083
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1541252
Clinical potential and experimental validation of prognostic genes in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by risk modeling utilizing single cell and transcriptome constructs
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the leading cause of tumor-related mortality worldwide. There is an urgent need for predictive biomarkers to guide treatment decisions. This study aimed to identify robust prognostic genes for HCC and to establish a theoretical foundation for clinical interventions.
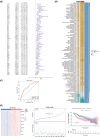
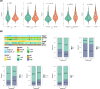
Methods: The HCC datasets were obtained from public databases and then differential expression analysis were used to obtain significant gene expression profiles. Subsequently, univariate Cox regression analysis and PH assumption test were performed, and a risk model was developed using an optimal algorithm from 101 combinations on the TCGA-LIHC dataset to pinpoint prognostic genes. Immune infiltration and drug sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the impact of these genes and to explore potential chemotherapeutic agents for HCC. Additionally, single-cell analysis was employed to identify key cellular players and their interactions within the tumor microenvironment. Finally, reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) was utilized to validate the roles of these prognostic genes in HCC.
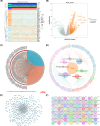
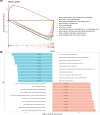
Results: A total of eight prognostic genes were identified (MCM10, CEP55, KIF18A, ORC6, KIF23, CDC45, CDT1, and PLK4). The risk model, constructed based on these genes, was effective in predicting survival outcomes for HCC patients. CEP55 exhibited the strongest positive correlation with activated CD4 T cells. The top 10 drugs showed increased sensitivity in the low-risk group. B cells were identified as key cellular components with the highest interaction numbers and strengths with macrophages in both HCC and control groups. Prognostic genes were more highly expressed in the initial state of B cell differentiation. RT-qPCR confirmed significant upregulation of MCM10, KIF18A, CDC45, and PLK4 in HCC tissues (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: This study successfully identified eight prognostic genes (MCM10, CEP55, KIF18A, ORC6, KIF23, CDC45, CDT1, and PLK4), which provided new directions for exploring the potential pathogenesis and clinical treatment research of HCC.
Keywords: combination algorithms; drug sensitivity; hepatocellular carcinoma; prognostic genes; single-cell sequencing analysis.
Copyright © 2025 Deng, Wang, Jiang, Xu, Zhang, Zhou, Gong, Lu, Hou and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


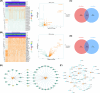
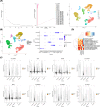
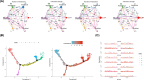
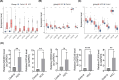
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

