Developing a Urinary Catheter with Anti-Biofilm Coated Surface Using Phyto-Assisted Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
- PMID: 40255461
- PMCID: PMC12008561
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S509957
Developing a Urinary Catheter with Anti-Biofilm Coated Surface Using Phyto-Assisted Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
Background: Biofilm-related infections represent one of the major challenging health problems that enhances antimicrobial resistance with subsequent treatment failure of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs).
Aim: This study aimed to employ and comprehensively characterize the use of nanoparticles to inhibit bacterial biofilm formation. Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) are considered one of the most important biofilm inhibitors.
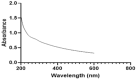
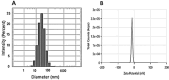
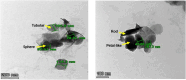
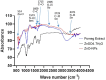
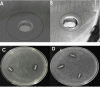
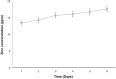
Methods: The current study aimed to characterize the influence of the bioreductive green synthesis of ZnO-NPs using pomegranate peel extract on bacterial colonization to protect against urinary catheter infections. ZnO-NPs were investigated for their physicochemical properties using UV, FTIR, Dynamic light scattering, and TEM. Catheters were coated with ZnO-NPs using Pistacia lentiscus (mastic), and the slow release of free zinc ions (Zn+2) from, the ZnO-NPs-coated catheters, was evaluated using the ICP-AES technique.
Results: The current study revealed that catheter coated by ZnO-NPs exhibited a sustained antibiofilm activity against biofilm-forming and antibiotic-resistant clinical isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains.
Conclusion: The present study supports the efficiency of ZnO-NPs as a good candidate for prevention of biofilm formation.
Keywords: bacterial colonization; biofilm; catheter associated infection; urinary catheters; zinc oxide nanoparticles.
© 2025 Goda et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Ukidave VV, Ingale LT. Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles from Coriandrum sativum and their use as fertilizer on Bengal gram, Turkish gram, and green gram plant growth. Inter J Agron. 2022;2022(1):8310038. doi: 10.1155/2022/8310038 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

