Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and 365-day mortality in patients with critical coronary heart disease
- PMID: 40255500
- PMCID: PMC12006011
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1513898
Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and 365-day mortality in patients with critical coronary heart disease
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to analyze the association between TyG-BMI and 365-day mortality in critically ill patients with CHD.
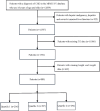
Methods: Patient data were extracted from the MIMIC-IV database. All patients were categorized into 3 groups based on TyG-BMI index: Low TyG-BMI index group, Medium TyG-BMI index group, and High TyG-BMI index group. Outcomes included primary and secondary outcomes, with the primary outcome being 365-day mortality and the secondary outcomes being hospital survival, intensive care unit (ICU) survival, and 28-day, 90-day, and 180-day mortality. The Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to compare the outcomes of the three groups. The relationship between TyG-BMI index and 365-day mortality was assessed using multivariate Cox proportional risk regression models and restricted cubic spline curves (RCS).
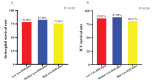
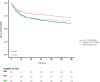
Results: 889 critically ill patients with CHD were analyzed. Among them, 600 (67.50%) were male patients with a mean age of 68.37 years and 289 (32.50%) were female patients with a mean age of 73.91 years. Patients with a medium TyG-BMI index had the best 365-day prognostic outcome and the highest survival rate compared with patients in the Low and High TyG-BMI index groups [201 (67.68%) vs. 166 (56.08%), 188 (63.51%); P=0.013]. After fully adjusted modeling analysis, the hazard ratio (HR) for 365-day mortality was found to be 0.71 (95% CI 0.54-0.93, P=0.012) for the Medium TyG-BMI index group. Meanwhile, RCS analysis showed an L-shaped relationship between TyG-BMI index and 365-day mortality.
Conclusions: The TyG-BMI index is significantly associated with 365-day mortality in patients with severe CHD.
Keywords: coronary heart disease (CHD); insulin resistance; mortality; prognosis; triglyceride glucose-body mass index (TyG-BMI).
Copyright © 2025 Tian, Dong, Xu, Ke and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Comment in
-
Commentary: Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and 365-day mortality in patients with critical coronary heart disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;16:1618817. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1618817. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40704147 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and mortality in intensive care unit patients: a propensity score matching analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 31;30(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-03128-8. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40887601 Free PMC article.
-
Association between trajectory of triglyceride-glucose index and all-cause mortality in critically ill patients with atrial fibrillation: a retrospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02838-x. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40640797 Free PMC article.
-
Association between triglyceride-glucose index and mortality in critically ill patients with atrial fibrillation: a retrospective cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Mar 24;24(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02697-6. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40128768 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose-body mass index and the incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 22;24(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02584-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39844258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between the triglyceride-glucose index and risk of cardiovascular diseases and mortality in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Jul 1;21(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01546-0. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35778731 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and mortality in intensive care unit patients: a propensity score matching analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 31;30(1):829. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-03128-8. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40887601 Free PMC article.
-
Commentary: Association between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and 365-day mortality in patients with critical coronary heart disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 25;16:1618817. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1618817. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40704147 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

