Peptides From Animal and Fishery Byproducts: Uplifting the Functionality of Fifth Quarter
- PMID: 40255552
- PMCID: PMC12006928
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70140
Peptides From Animal and Fishery Byproducts: Uplifting the Functionality of Fifth Quarter
Abstract
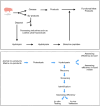
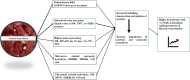
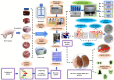
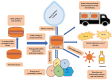
The meat and fish sectors are primary sources of animal protein for human consumption. However, they also generate large volumes of byproducts and organic waste annually, posing major challenges in terms of sustainable disposal. These byproducts have the potential to be repurposed into high-value, low-volume products, such as bioactive peptides or hydrolysates. Various methods used for the recovery of bioactive peptides from meat byproducts are enzymatic hydrolysis, microbial fermentation, ultrasonic-assisted, pulsed electric field, high hydrostatic pressure, microwave-assisted, and subcritical water processing. These bioactive peptides possess various functional properties, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, and antihypertensive effects. Incorporating them into food products could enhance both the functionality and quality of these products. In light of growing consumer demand for natural, eco-friendly ingredients, as well as sustainable practices in food production and packaging, the generation and use of bioactive peptides and hydrolysates offer a promising strategy. This approach not only mitigates environmental challenges but also fosters the sustainable growth of the meat and fishery industries, ensuring long-term ecological and economic viability. This review explores new opportunities and avenues for utilizing animal and marine byproducts in producing bioactive peptides and their potential applications in meat products and processing techniques, thereby supporting the sustainable growth of the meat and fishery industries.
Keywords: antimicrobial; antioxidant; functional activity; packaging; peptides; sensory attributes.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unlocking the potential of fishery waste: exploring diverse applications of fish protein hydrolysates in food and nonfood sectors.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025 Mar 22. doi: 10.1007/s11356-025-36244-3. Online ahead of print. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2025. PMID: 40119992 Review.
-
A review on bioactive peptides derived from meat and by-products: Extraction methods, biological activities, applications and limitations.Meat Sci. 2023 Oct;204:109278. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2023.109278. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Meat Sci. 2023. PMID: 37442015 Review.
-
Protein Hydrolysates from Fishery Processing By-Products: Production, Characteristics, Food Applications, and Challenges.Foods. 2023 Dec 13;12(24):4470. doi: 10.3390/foods12244470. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Valorisation of Agri-Food Waste for Bioactive Compounds: Recent Trends and Future Sustainable Challenges.Molecules. 2024 Apr 29;29(9):2055. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092055. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38731546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From waste to value: Integrating legume byproducts into sustainable industrialization.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 May;24(3):e70174. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70174. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 40260833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdelhedi, O. , Nasri R., Jridi M., et al. 2018. “Composite Bioactive Films Based on Smooth‐Hound Viscera Proteins and Gelatin: Physicochemical Characterization and Antioxidant Properties.” Food Hydrocolloids 74: 176–186. 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.08.006. - DOI
-
- Abu‐Salem, F. M. , Mahmoud M. H., El‐Kalyoubi M. H., Gibriel A. Y., and Arab A. A. A.. 2014. “Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of Peptides as Bioactive Components in Beef Burger.” International Journal of Nutrition and Food Engineering 8, no. 7: 763–771. 10.5281/zenodo.1096057. - DOI
-
- Ahmed, R. , and Chun B. S.. 2018. “Subcritical Water Hydrolysis for the Production of Bioactive Peptides From Tuna Skin Collagen.” Journal of Supercritical Fluids 141: 88–96. 10.3390/molecules26216655. - DOI
-
- Alemán, A. , Pérez‐Santín E., Bordenave‐Juchereau S., Arnaudin I., Gómez‐Guillén M. C., and Montero P.. 2011. “Squid Gelatin Hydrolysates With Antihypertensive, Anticancer and Antioxidant Activity.” Food Research International 44, no. 4: 1044–1051. 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.03.010. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

