The efficacy of different doses of citicoline in improving the prognosis of patients with acute ischemic stroke based on network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40255575
- PMCID: PMC12006040
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1529647
The efficacy of different doses of citicoline in improving the prognosis of patients with acute ischemic stroke based on network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: Our group aimed to explore the effect of different dosages of citicoline on ischemic stroke (IS) patients and determine the most appropriate dosage for these patients.
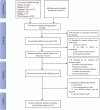
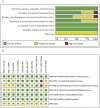
Methods: The databases of PubMed, Cochrane Library, Medline, Web of Science, and Embase were searched from their establishment to 15 October 2024. We assessed the quality of all included articles by using the Cochrane quality evaluation method or Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), which was based on the study type. Relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used for dichotomous data, and mean and standardized difference (SD) were used for continuous data. The outcome indicators were death, improvement in neurological function and daily living activities, and adverse effects.
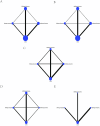
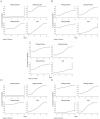
Results: In this study, a total of 13 studies were included. Of these, 370 patients were treated with 500 mg citicoline, 502 patients were treated with 1,000 mg citicoline, 1,891 patients were treated with 2,000 mg citicoline, and 2,582 patients were treated in the group of control (CON). We evaluated the treatment effect of different outcome indicators by ranking. In terms of death, both 500 mg citicoline and 2,000 mg citicoline demonstrated lower mortality than CON, with 2,000 mg citicoline having the lowest mortality. In terms of neurological function improvement, we found that compared to CON, the rates of improvement were higher and the rates of ineffective results were lower in 500-mg citicoline, 2,000-mg citicoline, and 1,000-mg citicoline groups. In terms of improvement in daily living activities, the MBI scores for 500 mg citicoline and 2000 mg citicoline were both higher than CON, while the MBI score for 1,000 mg citicoline was not. Lastly, in the aspect of adverse effects, we found that the rate of adverse effects was lower for 1,000 mg citicoline than CON, while it was higher for 500 mg citicoline and 2,000 mg citicoline.
Conclusion: Our research findings revealed that different dosages of citicoline significantly affect the neurological function, daily living activities, and adverse effects in patients with acute IS. Notably, 500 mg citicoline and 2,000 mg citicoline not only demonstrate higher rates of improvement in neurological function and daily living activities but also have lower mortality and ineffective results. However, this study does not specify the best one of the two dosages.
Keywords: citicoline; daily living activities; ischemic stroke; network meta-analysis; neurological function.
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Huo, Meng, Zhao, Liu, Chen, Mao and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy analysis of neuroprotective drugs in patients with acute ischemic stroke based on network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 7;15:1475021. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1475021. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39575393 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of oral citicoline in acute ischemic stroke: drug surveillance study in 4,191 cases.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;31(3):171-6. doi: 10.1358/mf.2009.31.3.1364241. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19536360 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral citicoline in acute ischemic stroke: an individual patient data pooling analysis of clinical trials.Stroke. 2002 Dec;33(12):2850-7. doi: 10.1161/01.str.0000038691.03334.71. Stroke. 2002. PMID: 12468781
-
A randomized efficacy trial of citicoline in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Stroke. 1999 Dec;30(12):2592-7. doi: 10.1161/01.str.30.12.2592. Stroke. 1999. PMID: 10582983 Clinical Trial.
-
Choline-Containing Phospholipids in Stroke Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):2875. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082875. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

