Immune regulation and clinical response of Chinese herbal injections combined with TACE in hepatocellular carcinoma: a cumulative logit regression and Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40255589
- PMCID: PMC12006906
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1567137
Immune regulation and clinical response of Chinese herbal injections combined with TACE in hepatocellular carcinoma: a cumulative logit regression and Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This study evaluated the immunomodulatory effects and clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal injections (CHIs) combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients using cumulative logit regression and Bayesian network meta-analysis.
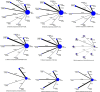
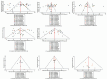
Methods: A systematic review of 48 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 4,293 HCC patients was conducted using PubMed, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Scopus, and Google Scholar. Outcomes included immune markers (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ ratio, and NK cells), clinical response rate, and overall survival (6-month, 1-year, and 2-year). Cumulative logit regression and Bayesian network meta-analysis were applied to synthesize ordinal and continuous outcomes.
Results: Compared to TACE alone, Aidi, Compound Kushen, and Huachansu significantly enhanced the immune function. Aidi increased CD3+ T cells (MD = 10.95, 95% CI: 8.04-13.86), CD4+ T cells (MD = 7.13, 4.37-9.89), CD4+/CD8+ ratio (MD = 0.31, 0.20-0.41), and NK cells (MD = 6.30, 4.49-8.12), while Compound Kushen showed the highest CD4+/CD8+ improvement (MD = 0.47, 0.37-0.56) and NK cell elevation (MD = 9.11, 7.32-10.91). Huachansu increased CD3+ T cells (MD = 8.74, 4.43-13.06) and CD4+ T cells (MD = 8.00, 4.21-11.80). For clinical outcomes, Compound Kushen (HR = 2.57, 1.9-3.59) and Aidi (HR = 2.28, 1.68-3.18) improved clinical response rates versus TACE. Aidi enhanced 6-month (OR = 2.57, 1.44-4.56) and 1-year survival (OR = 2.46, 1.56-3.88), whereas Huachansu (OR = 3.47, 2.42-4.97) and Compound Kushen (OR = 2.91, 1.07-7.89) improved 2-year survival.
Conclusion: Aidi, Compound Kushen, and Huachansu enhance immune function and survival in HCC patients when combined with TACE. Compound Kushen showed the most significant immunomodulatory effects, while Aidi and Huachansu improved short- and long-term survival, respectively. Further high-quality head-to-head RCTs are required to validate these results.
Keywords: Bayesian network meta-analysis; Chinese herbal injections; cumulative logit regression; hepatocellular carcinoma; transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Copyright © 2025 Gu, Zhu, Zhang, Xue and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative efficacy of Chinese herbal injections for treating endometrial carcinoma: A Bayesian network meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Oct 13;102(41):e34676. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034676. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37832073 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Chinese Herbal Injections Combined With Cyclophosphamide and 5-Fluorouracil Chemotherapies in Treatment of Breast Cancer: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 27;11:572396. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.572396. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33708106 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Aidi injection plus transarterial chemoembolization on primary hepatic carcinoma: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2017 Oct;37(5):567-587. J Tradit Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 32188217
-
Efficacy and Safety of Aidi Injection Combined with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization on Primary Hepatic Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Jul 24;2018:6376429. doi: 10.1155/2018/6376429. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30140297 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of Chinese medicine injections combined with capecitabine and oxaliplatin chemotherapies in treatment of colorectal cancer: A bayesian network meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Nov 29;13:1004259. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1004259. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36523501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Q, Liu J, Li T, Zhou C, Wang Y, Huang S, et al. . Comparison of DEB-TACE and cTACE for the initial treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma beyond up-to-seven criteria: a single-center propensity score matching analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2022) 46:101893. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2022.101893, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

