Role of the endothelial cell glycocalyx in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 40255592
- PMCID: PMC12006053
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1535673
Role of the endothelial cell glycocalyx in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
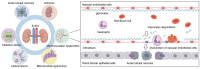
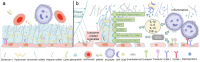
Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (S-AKI) is a common complication of sepsis. It occurs at high incidence and is associated with a high level of mortality in the intensive care unit (ICU). The pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying S-AKI are complex, and include renal vascular endothelial cell dysfunction. The endothelial glycocalyx (EG) is a polysaccharide/protein complex located on the cell membrane at the luminal surface of vascular endothelial cells that has anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic, and endothelial protective effects. Recent studies have shown that glycocalyx damage plays a causal role in S-AKI progression. In this review, we first describe the structure, location, and basic function of the EG. Second, we analyze the underlying mechanisms of EG degradation in sepsis and S-AKI. Finally, we provide a summary of the potential therapeutic strategies that target the EG.
Keywords: endothelium; glycocalyx; inflammation; kidney; sepsis.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Zhang, Qu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx.Crit Care Clin. 2020 Apr;36(2):217-232. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2019.12.007. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Crit Care Clin. 2020. PMID: 32172810 Review.
-
Glycocalyx and sepsis-induced alterations in vascular permeability.Crit Care. 2015 Jan 28;19(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0741-z. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25887223 Free PMC article.
-
Increased R-spondin 3 contributes to aerobic exercise-induced protection against renal vascular endothelial hyperpermeability and acute kidney injury.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023 Dec;239(4):e14036. doi: 10.1111/apha.14036. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2023. PMID: 37607126
-
The Endothelial Glycocalyx: New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches in Sepsis.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3758278. doi: 10.1155/2016/3758278. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27699168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HYAL1 deficiency attenuates lipopolysaccharide-triggered renal injury and endothelial glycocalyx breakdown in septic AKI in mice.Ren Fail. 2023 Dec;45(1):2188966. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2188966. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37563795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song MJ, Jang Y, Legrand M, Park S, Ko R, Suh GY, et al. . Epidemiology of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a multicenter, prospective, observational cohort study in South Korea. Crit Care Lond Engl. (2024) 28:383. doi: 10.1186/s13054-024-05167-9, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanski NL, Cvijanovich NZ, Fitzgerald JC, Bigham MT, Wong HR. Genomics of pediatric septic shock investigators. Severe acute kidney injury is independently associated with mortality in children with septic shock. Intensive Care Med. (2020) 46:1050–1. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-05940-8, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

