Distinct infectivity and neutralization antibody responses in the highly homologous AAV Go.1 and AAV5
- PMID: 40255594
- PMCID: PMC12006905
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1554449
Distinct infectivity and neutralization antibody responses in the highly homologous AAV Go.1 and AAV5
Abstract
Introduction: Goat-derived adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors, such as AAV Go.1, represent a novel platform for gene therapy due to their unique origin and potential advantages in transduction efficiency and immune evasion. However, their therapeutic potential and biological properties remain underexplored.
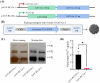
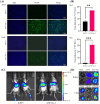
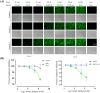
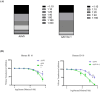
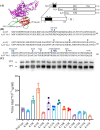
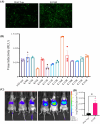
Methods: In this study, we developed a recombinant AAV (rAAV) Go.1 by replacing the goat AAV rep gene with the standard AAV2-rep gene to improve packaging efficiency. We compared the transduction efficiency of rAAV Go.1 with that of AAV5, a closely related serotype with 95% genome similarity, both in vitro and in vivo. Additionally, we assessed immune evasion properties by evaluating resistance to neutralization using sera from rAAV5-immunized mice and human volunteers. To further enhance transduction efficiency, we introduced site-specific mutations in the VP1 unique (VP1u) region and VP1/2 common region.
Results: The rep gene modification led to a significantly higher packaging efficiency for rAAV Go.1 compared to the original goat AAV. rAAV Go.1 exhibited markedly higher transduction efficiency than AAV5 in both in vitro and in vivo models. Furthermore, rAAV Go.1 demonstrated a 4-fold increase in resistance to neutralization by sera from rAAV5-immunized mice. A study involving 20 healthy volunteers revealed that high-titer neutralizing antibodies had a more pronounced inhibitory effect on rAAV5 compared to rAAV Go.1. Mutagenesis studies identified key modifications that enhanced viral properties: K32R, K91R, and K122R mutations in the VP1u region significantly improved viral production, while K137R (VP1u) enhanced transduction efficiency in vitro and in vivo.
Discussion: Our findings highlight the potential of rAAV Go.1 as an improved gene therapy vector with superior transduction efficiency and enhanced immune evasion. The identified VP1 mutations further optimize viral properties, making rAAV Go.1 a promising candidate for future therapeutic applications.
Keywords: cell transfection; gene therapy; neutralizing antibody; packaging efficiency; rAAV Go.1.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Ma, Wu, Gao, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improved Genome Packaging Efficiency of Adeno-associated Virus Vectors Using Rep Hybrids.J Virol. 2021 Sep 9;95(19):e0077321. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00773-21. Epub 2021 Jul 21. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34287038 Free PMC article.
-
OneBac 2.0: Sf9 Cell Lines for Production of AAV5 Vectors with Enhanced Infectivity and Minimal Encapsidation of Foreign DNA.Hum Gene Ther. 2015 Oct;26(10):688-97. doi: 10.1089/hum.2015.050. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Hum Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 26134901 Free PMC article.
-
OneBac 2.0: Sf9 Cell Lines for Production of AAV1, AAV2, and AAV8 Vectors with Minimal Encapsidation of Foreign DNA.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2017 Feb;28(1):15-22. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2016.164. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2017. PMID: 28125901 Free PMC article.
-
AAV- based vector improvements unrelated to capsid protein modification.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 3;10:1106085. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1106085. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36817775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adeno-Associated Virus Engineering and Load Strategy for Tropism Modification, Immune Evasion and Enhanced Transgene Expression.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 29;19:7691-7708. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S459905. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39099791 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

