The Pathogenesis of Oxidative Stress-Induced Chloasma and Its Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 40255635
- PMCID: PMC12009569
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S520625
The Pathogenesis of Oxidative Stress-Induced Chloasma and Its Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
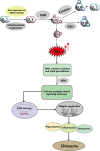
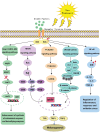
The majority of oral and topical skin-whitening products, as well as chemical peels, are commonly used to treat chloasma, a challenging skin pigmentation disorder. However, the therapeutic efficacy of these treatments often falls short of patients' expectations and is accompanied by notable side effects. Oxidative stress, characterized by an imbalance between oxidation and antioxidation, plays a crucial role in various clinical conditions and leads to oxidative damage, including cellular dysfunction, DNA damage, protein and lipid peroxidation, and even irreversible cell death. Recent research has shown that the onset of chloasma is closely associated with oxidative stress. This review explores the role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of chloasma and examines the related signaling pathways and biomarkers. Our findings suggest that antioxidant therapy can enhance the effectiveness of chloasma treatment by inhibiting tyrosinase activity and reducing melanin production. We hope this review will provide a theoretical foundation for future antioxidant-based treatments for chloasma.
Keywords: antioxidant therapy; chloasma; oxidative stress; pathogenesis; review.
© 2025 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin D and wound healing: Assessing skin barrier function and implications for chloasma treatment.Int Wound J. 2024 Jan;21(1):e14541. doi: 10.1111/iwj.14541. Int Wound J. 2024. Retraction in: Int Wound J. 2025 Apr;22(4):e70481. doi: 10.1111/iwj.70481. PMID: 38272820 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
Oral intake of proanthocyanidin-rich extract from grape seeds improves chloasma.Phytother Res. 2004 Nov;18(11):895-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1537. Phytother Res. 2004. PMID: 15597304 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical Development and Evaluation of a Multi-Component Dissolving Microneedle Patch for Skin Pigmentation Disorders.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Aug 4;15(15):3296. doi: 10.3390/polym15153296. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571190 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress products and managements in atopic dermatitis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 9;12:1538194. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1538194. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40417699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of PRP in Chloasma: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Apr 7;2022:7487452. doi: 10.1155/2022/7487452. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35432505 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Polysaccharides of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz alleviate bursa of Fabricius involution in Magang geese by inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105227. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105227. Epub 2025 May 1. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40339240 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources