The Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potentials of Dendritic Cells in NSCLC
- PMID: 40255658
- PMCID: PMC12007507
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S506644
The Emerging Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potentials of Dendritic Cells in NSCLC
Abstract
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the predominant subtype of lung cancer. Despite the demonstrated effectiveness of established treatments such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy, the prognosis for patients with advanced NSCLC remains poor. Dendritic cells (DCs), the most potent antigen-presenting cells (APCs), play a crucial role in the tumor microenvironment (TME) of NSCLC. This review explores the classification and biological functions of DCs, highlighting the specific molecular pathways and external factors that influence their maturation and function in NSCLC, which is novel in this review. Moreover, we discuss the potential therapeutic applications of DCs in the management of NSCLC, presenting novel possibilities for future treatments.
Keywords: dendritic cells; maturation; non-small-cell lung cancer; treatment.
© 2025 Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. Figures were created by Figdraw (www.figdraw.com).
Figures
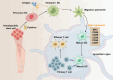
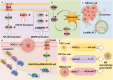
References
-
- Liu Y, Yin Z, Lu P, et al. Lung carcinoma cells secrete exosomal MALAT1 to inhibit dendritic cell phagocytosis, inflammatory response, costimulatory molecule expression and promote dendritic cell autophagy via AKT/mTOR pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:10693–10705. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S256669 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

