Exploring Acute Pancreatitis After Orlistat Use: A Case Report
- PMID: 40255727
- PMCID: PMC12007682
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80832
Exploring Acute Pancreatitis After Orlistat Use: A Case Report
Abstract
Orlistat is an FDA-approved medication for obesity management that functions as a pancreatic lipase inhibitor. This medication is accessible without a prescription in numerous developed nations. As its utilization rises, the likelihood of experiencing adverse events also increases. A thorough understanding of these events is crucial for making informed decisions and ensuring effective management. We describe the case of a 23-year-old female who presented with acute pancreatitis after she started orlistat. We reviewed the association between orlistat use and acute pancreatitis, analyzing clinical cases and potential risk factors. By examining available medical literature and case studies, our study aims to provide insights into the correlation between orlistat therapy and the manifestation of acute pancreatitis.
Keywords: calcium; drug-induced; etiology; orlistat; pancreatitis; risk factor; s: orlistat.
Copyright © 2025, Qasim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
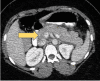

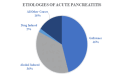

Similar articles
-
Acute pancreatitis following orlistat therapy: report of two cases.JOP. 2010 Jan 8;11(1):61-3. JOP. 2010. PMID: 20065556
-
An Unexpected Result of Obesity Treatment: Orlistat-Related Acute Pancreatitis.Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2015 May 8;9(2):152-5. doi: 10.1159/000430433. eCollection 2015 May-Aug. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26078734 Free PMC article.
-
36 year old man presenting with pancreatitis and a history of recent commencement of Orlistat case report.Nutr J. 2006 Aug 28;5:19. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-5-19. Nutr J. 2006. PMID: 16938137 Free PMC article.
-
Modern medical management of obesity: the role of pharmaceutical intervention.J Am Diet Assoc. 1998 Oct;98(10 Suppl 2):S23-6. doi: 10.1016/s0002-8223(98)00706-8. J Am Diet Assoc. 1998. PMID: 9787732 Review.
-
Orlistat-associated adverse effects and drug interactions: a critical review.Drug Saf. 2008;31(1):53-65. doi: 10.2165/00002018-200831010-00005. Drug Saf. 2008. PMID: 18095746 Review.
References
-
- Burden of gastrointestinal disease in the United States: 2012 update. Peery AF, Dellon ES, Lund J, et al. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016508512011572. Gastroenterology. 2012;143:1179–1187. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: a review. Jones MR, Hall OM, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. https://www.ochsnerjournal.org/content/15/1/45.short. Ochsner J. 2015;15:45–51. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drug-induced pancreatitis: a critical review. Mallory A, Kern F. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/0016508580906897. Gastroenterology. 1980;78:813–820. - PubMed
-
- Orlistat‑induced acute pancreatitis in a type II diabetic and hypothyroid young woman: a case report. Chaudhuri PR, Santra R, Palodhi S, Mondal S. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Ranjita-Santra/publication/29133680... Int J Health Allied Sci. 2013;2:278–282.
-
- Orlistat-associated adverse effects and drug interactions: a critical review. Filippatos TD, Derdemezis CS, Gazi IF, Nakou ES, Mikhailidis DP, Elisaf MS. https://link.springer.com/article/10.2165/00002018-200831010-00005. Drug Saf. 2008;31:53–65. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
