Segond Fracture: From X-ray to Surgical Treatment
- PMID: 40255786
- PMCID: PMC12007960
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80849
Segond Fracture: From X-ray to Surgical Treatment
Abstract
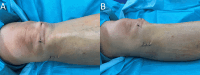
Segond fracture is an avulsion fracture of the lateral side of the tibial plateau. In most cases, this fracture is associated with serious injuries to the knee such as a rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). This highlights the importance of recognizing and diagnosing such fractures on X-ray images followed by the use of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), in order to accurately diagnose potential additional injuries of the knee joint. This report shows relevant images as well as the outcome of a 59-year-old woman with a right-sided Segond fracture.
Keywords: arthroscopy; ct; mri; segond fracture; trauma surgery; x-ray.
Copyright © 2025, Adwan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures





References
-
- Achtnich AE, Akoto R, Barié A, et al. AGA Committee Knee Ligament; 2016. Diagnosis of the knee ligament system (Book in German)
-
- Skinner EJ, Davis DD, Varacallo MA. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Segond fracture. - PubMed
-
- Avulsion fracture of the medial collateral ligament association with Segond fracture. Albtoush OM, Horger M, Springer F, Fritz J. Clin Imaging. 2019;53:32–34. - PubMed
-
- The Segond fracture of the proximal tibia: a small avulsion that reflects major ligamentous damage. Goldman AB, Pavlov H, Rubenstein D. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;151:1163–1167. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
