Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced Performance on Diagnostic Radiology In-Training Exams
- PMID: 40255788
- PMCID: PMC12009162
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.80874
Comparative Analysis of ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced Performance on Diagnostic Radiology In-Training Exams
Abstract
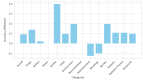
Background The increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in medical education and clinical practice has led to a growing interest in large language models (LLMs) for diagnostic reasoning and training. LLMs have demonstrated potential in interpreting medical text, summarizing findings, and answering radiology-related questions. However, their ability to accurately analyze both written and image-based content in radiology remains uncertain with newer models. This study evaluates the performance of OpenAI's Chat Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4o (ChatGPT-4o) and Google DeepMind's Gemini Advanced on the 2022 ACR (American College of Radiology) Diagnostic Radiology In-Training (DXIT) Exam to assess their capabilities in different radiological subfields. Methods ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced were tested on 106 multiple-choice questions from the 2022 DXIT exam, which included both image-based and written-based questions spanning various radiological subspecialties. Their performance was compared using overall accuracy, subfield-specific accuracy, and two-proportion z-tests to determine significant differences. Results ChatGPT-4o achieved an overall accuracy of 69.8% (74/106), outperforming Gemini Advanced, which scored 60.4% (64/106), although the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.151). In image-based questions (n = 64), ChatGPT-4o performed better (57.8%, 37/64) than Gemini Advanced (43.8%, 28/64). For written-based questions (n = 42), ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced demonstrated similar accuracy (88.1% vs. 85.7%). ChatGPT-4o exhibited stronger performance in specific subfields, such as cardiac and nuclear radiology, but neither model showed consistent superiority across all radiology domains. Conclusion LLMs show promise in radiology education and diagnostic reasoning, particularly for text-based assessments. However, limitations such as inconsistent responses and lower accuracy in image interpretation highlight the need for further refinement. Future research should focus on improving AI models' reliability, multimodal capabilities, and integration into radiology training programs.
Keywords: artificial intelligence in radiology; chat gpt; chatgpt-4o; gemini advanced; radiology medical education.
Copyright © 2025, Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy and quality of ChatGPT-4o and Google Gemini performance on image-based neurosurgery board questions.Neurosurg Rev. 2025 Mar 25;48(1):320. doi: 10.1007/s10143-025-03472-7. Neurosurg Rev. 2025. PMID: 40131528
-
Evaluating text and visual diagnostic capabilities of large language models on questions related to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System Atlas 5th edition.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025 Mar 3;31(2):111-129. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.242876. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39248152 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of ChatGPT-4o mini, ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 16;26(1):369. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08601-3. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40241048 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Large Language Models When Answering Clinical Research Questions: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.J Med Internet Res. 2025 Apr 30;27:e64486. doi: 10.2196/64486. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40305085 Free PMC article.
-
ChatGPT and radiology report: potential applications and limitations.Radiol Med. 2024 Dec;129(12):1849-1863. doi: 10.1007/s11547-024-01915-7. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Radiol Med. 2024. PMID: 39508933 Review.
References
-
- The performance of artificial intelligence-based large language models on ophthalmology-related questions in Swedish proficiency test for medicine: ChatGPT-4 omni vs Gemini 1.5 Pro. Sabaner MC, Hashas ASK, Mutibayraktaroglu KM, Yozgat Z, Klefter ON, Subhi Y. AJO International. 2024;1
-
- Optimizing AI language models: a study of ChatGPT-4 vs. ChatGPT-4o [PREPRINT] Siddiky AM, Rahman ME, Hossen FB, Rahman MR, Jaman S. Preprints. 2025
-
- Evaluating the effectiveness of advanced large language models in medical knowledge: a comparative study using Japanese national medical examination. Liu M, Okuhara T, Dai Z, et al. Int J Med Inform. 2025;193:105673. - PubMed
-
- ChatGPT vs Gemini: comparative accuracy and efficiency in CAD-RADS score assignment from radiology reports. Silbergleit M, Tóth A, Chamberlin JH, et al. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 - PubMed
-
- Performance of GPT-4 on the American College of Radiology In-training Examination: evaluating accuracy, model drift, and fine-tuning. Payne DL, Purohit K, Borrero WM, et al. Acad Radiol. 2024;31:3046–3054. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
