Splicing correction by peptide-conjugated morpholinos as a novel treatment for late-onset Pompe disease
- PMID: 40255904
- PMCID: PMC12008586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2025.102524
Splicing correction by peptide-conjugated morpholinos as a novel treatment for late-onset Pompe disease
Abstract
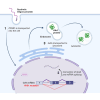
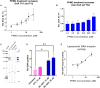
Late-onset Pompe disease (LOPD) is overwhelmingly caused by a single mutation that disrupts splicing of acid-alpha glucosidase (GAA) and results in the accumulation of lysosomal glycogen in muscle cells leading to progressive muscle weakness in patients. Current therapeutics for LOPD do not meet the needs of patients and have largely been developed in mutant animal models lacking Gaa expression, which more closely mimic the less common infantile form of the disease. Here we design and evaluate peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PPMOs) to target the causative mutation in GAA and correct pathogenic splicing in muscle tissue. We show PPMO compounds correct LOPD splicing in both patient induced pluripotent stem cell-derived muscle cells and in skeletal muscle tissue after intravenous dosing in a newly developed humanized LOPD animal model that recapitulates patient LOPD splicing.
Keywords: MT: Oligonucleotides: Therapies and Applications; RNA medicines; late-onset Pompe disease; lysosomal storage disease; oligonucleotide therapeutics; splice switching antisense oligonucleotide.
© 2025 Sarepta Therapeutics, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors were employees of Sarepta Therapeutics during the course of this work. R.A.O. is currently an employee of Aliada Therapeutics. M.E.A. is currently an employee of Jnana Therapeutics. T.J. is currently an employee of Editas Medicines. X.T. is currently an employee of Intellia Therapeutics. A.J.C. is currently an employee of Amgen. K.J.K. is currently an employee of MiRecule. A.B.M. is currently an employee of Foresite Labs. Two patents cover this work: Pompe Disease Mouse Model Generation, Characterization and Methods of Use Pompe Disease Mouse Model Generation, Characterization and Methods of Use US patent application 63/377,516 WO/2024/073404 · September 26, 2023. Antisense Oligonucleotides Having One or More Abasic Subunits Antisense Oligonucleotides Having One or More Abasic Subunits US patent application US2022/044995 WO/2023/055774A1 · September 28, 2022.
Figures





References
-
- Hagemans M.L.C., Winkel L.P.F., Van Doorn P.A., Hop W.J.C., Loonen M.C.B., Reuser A.J.J., Van der Ploeg A.T. Clinical manifestation and natural course of late-onset Pompe's disease in 54 Dutch patients. Brain. 2005;128:671–677. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

