Intravitreal low-dose triamcinolone acetonide for nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
- PMID: 40256032
- PMCID: PMC11947530
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2025.04.13
Intravitreal low-dose triamcinolone acetonide for nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravitreal low-dose (1 mg) triamcinolone acetonide (TA) in Chinese acute nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) patients.
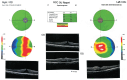
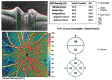
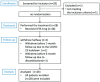
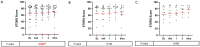
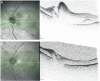
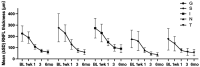
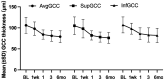
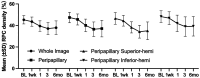
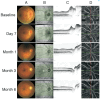
Methods: Twenty-eight eyes of 28 patients with acute NAION (<30d of visual acuity loss) were enrolled and given intravitreal TA (IVTA) once. Visual field (VF), best corrected visual acuity (BCVA), retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) thickness, ganglion cell complex (GCC) thickness, radial peripapillary capillary (RPC) density, and intraocular pressure (IOP) were evaluated at baseline and 7d, 1, 3, and 6mo after IVTA.
Results: VF and BCVA were significant improved during the follow-up according to the mean deviation (MD), visual field index (VFI), and Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) scores (all P<0.001). There was no significant difference between the group that received an injection less than 14d after illness onset and the group that received an injection more than 14d after illness onset. The RNFL thickness, GCC thickness and RPC density were significantly decreased (all P<0.001). Temporary ocular hypertension was present in five eyes.
Conclusion: Low-dose IVTA may be an alternative safe treatment option for some NAION patients in the acute stage. However, optic nerve atrophy still existed.
Keywords: intravitreal injections; nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy; triamcinolone acetonide; visual acuity; visual field.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Liu ZJ, None; Xu X, None; Lyu YN, None; Li DL, None; Zhou H, None; Gong YY, None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intravitreal triamcinolone injections in non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy - A retrospective report.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021 Jun;44(6):777-785. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2020.07.027. Epub 2021 May 27. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2021. PMID: 34053770
-
Combination Therapy with Intravitreal Triamcinolone Acetonide and Oral Levodopa for the Treatment of Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: A Pilot Study.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Mar;38(2):167-175. doi: 10.1089/jop.2021.0081. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35049379
-
The effect of an intravitreal triamcinolone acetonide injection for acute nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009 Mar;23(1):59-61. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.1.59. Epub 2009 Mar 9. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19337484 Free PMC article.
-
[Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy animal model and its treatment applications].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014 Apr;118(4):331-61. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 24864434 Review. Japanese.
-
Intravitreal steroids for macular edema in diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 17;11(11):CD005656. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005656.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33206392 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
