Evidence-Based Bibliometric Analysis of Acupuncture in Functional Dyspepsia: Clinical Efficacy and Research Trends
- PMID: 40256110
- PMCID: PMC12009576
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S515144
Evidence-Based Bibliometric Analysis of Acupuncture in Functional Dyspepsia: Clinical Efficacy and Research Trends
Abstract
Objective: The method of bibliometric analysis was used to visualize the literature data of the current research on acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia.
Methods: By using the bibliometrix package in R4.4.1, all the research literatures related to acupuncture and moxibustion treatment of functional dyspepsia in the WOS core database were used, and the data visualization analysis of the retrieved research literatures was carried out.
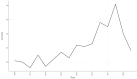
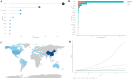
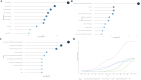
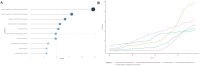
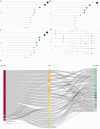
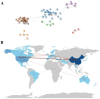
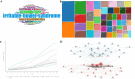
Results: A total of 489 research literatures on acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia were screened out. The earliest related research was published in 2009. After 2013, the research heat in this field increased rapidly, reaching its peak in 2022. The number of publications and citations related to acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia in China ranked first. Analysis of cumulative publication volume shows that from 2012 to 2024, JEVIDENCE-BASED COMPLEMENTARY AND ALTERNATIVE MEDIC ranked first in cumulative publication volume. A total of 1841 authors contributed to this field. The top three authors were WU HG, LIU HR and LI Y. WU HG ranked first in author influence and citation frequency. The most frequently used keyword in the articles published by these authors was "irritable-bowel-syndrome". The high-frequency keywords in the literature on acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia were statistically analyzed. The top three high-frequency words were irritable-bowel-syndrome, followed by acupuncture and electroacupuncture.
Conclusion: Acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia related research was first published in 2009, the research heat increased year by year. The most authoritative author in the field of acupuncture treatment of functional dyspepsia is WU HG.
Keywords: acupuncture; bibliometric; functional dyspepsia.
© 2025 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
XinJing Wei and XiaoFei Jia are co-first authors for this study. All of the authors had no any personal, financial, commercial, or academic conflicts of interest separately for this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Medication Compliance in Children with Asthma.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025 May 23;18:2875-2887. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S514612. eCollection 2025. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40433421 Free PMC article.
-
[Bibliometric analysis on the literature characteristics of animal experiment research with acupuncture and moxibustion].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Dec 25;47(12):1123-9. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220766. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36571230 Chinese.
-
Bibliometric analysis of functional dyspepsia research trends over the past 20 years.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 23;10:1019110. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1019110. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36504925 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends of acupuncture therapy on stress urinary incontinence from 1992 to 2022: A bibliometric analysis.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 1;9(9):e19732. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19732. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37810054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research trends in the field of the gut-brain interaction: Functional dyspepsia in the spotlight - An integrated bibliometric and science mapping approach.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 8;17:1109510. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1109510. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36968499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sander GB, Mazzoleni LE, Francesconi CF, et al. Helicobacter eradication relief of dyspeptic symptoms trial investigators. Influence of organic and functional dyspepsia on work productivity: the HEROES-DIP study. Value Health. 2011;14(5 Suppl 1):S126–9. PMID: 21839884. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2011.05.021 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

