Enhanced reno-protective effects of CHIR99021 modified mesenchymal stem cells against rat acute kidney injury model
- PMID: 40256225
- PMCID: PMC12008493
- DOI: 10.34172/bi.30600
Enhanced reno-protective effects of CHIR99021 modified mesenchymal stem cells against rat acute kidney injury model
Abstract
Introduction: Mesenchymal stem cells of human umbilical cord origin (hucMSCs) appear to be an attractive candidate for cell-based therapies. However, their efficacy requires improvement as poor survival and specific homing to the site of injury are the major barriers to their effective implementation in cell therapy. As Wnt signaling pathway is involved in the development and repair of organs, we adopted a preconditioning strategy of stem cells by using CHIR99021 compound (a Wnt pathway agonist) to potentiate hucMSCs beneficial effects and circumvent their therapeutic limitations.
Methods: We treated hucMSCs with 5 µM of CHIR99021 and evaluated the expression levels of genes involved in different biological processes through qRT-PCR. Subsequently, we examined the effectiveness of preconditioned cells (CHIR99021-hucMSCs) in a cisplatin-induced rat acute kidney injury model. Amelioration in tissue injury was evaluated by histopathology, immunohistochemistry and renal functional assessment.
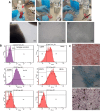
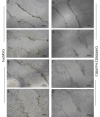
Results: In treated groups, we observed preserved renal tissue architecture in terms of lesser epithelial cells necrosis (P ≤ 0.001) and cast formation ( ≤ 0.05). Accelerated proliferation of injured tubular cells (P ≤ 0.001) and low serum creatinine values (P ≤ 0.01) were observed in preconditioned hucMSCs group compared to untreated AKI rats. In addition, administration of preconditioned hucMSCs in kidney injury model offered better restoration of tubular cell membrane β-catenin molecules. Our findings showed that CHIR99021-modified hucMSCs may exhibit better capacity for cell migration and proliferation.
Conclusion: The results showed that preconditioning of stem cells with Wnt pathway activators could provide advanced benefits for organ repair, which may contribute to design a more effective therapeutic approach for renal regeneration.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Mesenchymal stem cells; Preconditioning; Regeneration; Stem cell therapy; Wnt signaling.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway enhances exosome production by hucMSCs and improves their capability to promote diabetic wound healing.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 26;22(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02650-x. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38926800 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte growth factor modification promotes the amelioration effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on rat acute kidney injury.Stem Cells Dev. 2011 Jan;20(1):103-13. doi: 10.1089/scd.2009.0495. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Stem Cells Dev. 2011. PMID: 20446811
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells attenuate cisplatin-induced acute and chronic renal injury.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013 Aug 1;238(8):960-70. doi: 10.1177/1535370213497176. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2013. PMID: 23970411
-
Resveratrol improves human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells repair for cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 20;9(10):965. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0959-1. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30237401 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Osteogenesis-Related Regulatory Mechanisms of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023 Jul;19(5):1252-1267. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10521-5. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2023. PMID: 36917312 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous