The multifaceted roles of extracellular vesicles in osteonecrosis of the femoral head
- PMID: 40256260
- PMCID: PMC12008682
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.03.009
The multifaceted roles of extracellular vesicles in osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Abstract
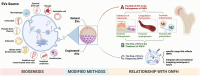
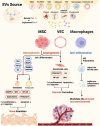
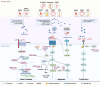
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) is a severe disease characterized by bone tissue necrosis due to vascular impairment, often leading to joint collapse and requiring surgical intervention. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) serve as crucial mediators of intercellular communication, influencing osteogenesis, angiogenesis, and immune regulation. This review summarizes the dual role of EVs in both the pathogenesis of ONFH and post-necrosis bone repair, highlighting the impact of various EV-mediated signaling pathways on bone regeneration and the potential crosstalk among these pathways. Additionally, EVs hold promise as diagnostic biomarkers or contrast agents to complement conventional imaging techniques for ONFH detection. By elucidating the role of EVs in osteonecrosis and addressing the current challenges, we aspire to establish a foundation for the timely identification and treatment of ONFH. The translational potential of this article: This review comprehensively discusses the role of EVs in ONFH, providing innovative and promising insights for its diagnosis and treatment, which also establishes a theoretical foundation for the future clinical application of EVs in ONFH.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; Mesenchymal stem cells; MicroRNA; Osteonecrosis of the femoral head; Pathogenesis.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A conflict of interest occurs when an individual's objectivity is potentially compromised by a desire for financial gain, prominence, professional advancement or a successful outcome. The Editors of the Journal of Orthopaedic Translation strive to ensure that what is published in the Journal is as balanced, objective and evidence-based as possible. Since it can be difficult to distinguish between an actual conflict of interest and a perceived conflict of interest, the Journal requires authors to disclose all and any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Extracellular vesicles from human urine-derived stem cells inhibit glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by transporting and releasing pro-angiogenic DMBT1 and anti-apoptotic TIMP1.Acta Biomater. 2020 Jul 15;111:208-220. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.020. Epub 2020 May 22. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32447063
-
microRNA-148a-3p in extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppresses SMURF1 to prevent osteonecrosis of femoral head.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Oct;24(19):11512-11523. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15766. Epub 2020 Sep 1. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32871042 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of extracellular vesicles in osteonecrosis of femoral head: A systematic review.Gene. 2021 Mar 10;772:145379. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145379. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33359121
-
Application of biomaterials in treating early osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Research progress and future perspectives.Acta Biomater. 2023 Jul 1;164:15-73. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.04.005. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37080444 Review.
-
Exploring of exosomes in pathogenesis, diagnosis and therapeutic of osteonecrosis of the femoral head: the mechanisms and signaling pathways.Biomed Mater. 2024 Aug 21;19(5). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ad6dc6. Biomed Mater. 2024. PMID: 39121885 Review.
Cited by
-
"Multidisciplinary synergy driving innovation in orthopaedic translational medicine".J Orthop Translat. 2025 Jun 4;52:A1-A3. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.06.001. eCollection 2025 May. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40698066 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Harnessing miRNA-Containing Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Regeneration of Bone Defects: A Narrative Review of Mechanisms, Biomaterials, and Clinical Translation.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 23;17(15):2438. doi: 10.3390/cancers17152438. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805141 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

