Diagnostic accuracy of automated breast volume scanning, hand-held ultrasound and molybdenum-target mammography for breast lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40256474
- PMCID: PMC12004323
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-24-135
Diagnostic accuracy of automated breast volume scanning, hand-held ultrasound and molybdenum-target mammography for breast lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Given the high incidence and increasing burden of breast cancer, more approaches are needed to improve the early diagnosis of breast cancer. The three mainstream diagnostic methods, automated breast volume scanning (ABVS), hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) and mammography, are still controversial in their diagnostic accuracy. The aim of this study is to systematically evaluate the accuracy of three diagnostic methods.
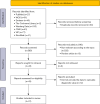
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, The Cochrane Library, Wanfang Data, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), VIP and SinoMed databases were searched by computer. Studies on the accuracy of ABVS, HHUS and mammography in the diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions were collected, and the search time limit was from the establishment of the database to August 2022. The Chi-square test was then performed using Meta-Disc software, and the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) tool was used for bias and quality assessment.
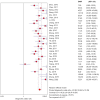
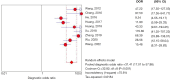
Results: A total of 31 studies involving 8,107 benign or malignant lesion were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, diagnostic odds ratio, and area under curve for HHUS were 0.86 (0.84, 0.87), 0.80 (0.78, 0.81), 4.20 (3.53, 4.99), 0.20 (0.16, 0.24), 22.88 (16.84, 31.08) and 0.898, respectively. And those for ABVS were 0.90 (0.89, 0.91), 0.87 (0.86, 0.88), 7.93 (5.05, 12.45), 0.11 (0.09, 0.15), 74.63 (45.37, 122.76) and 0.956, respectively. And those for molybdenum-target mammography were 0.81 (0.78, 0.84), 0.90 (0.88, 0.91), 6.94 (4.32, 11.17), 0.23 (0.18, 0.29), 31.41 (17.01, 57.98) and 0.887, respectively. Indicators related to patient selection and reference standards suggested a high risk of bias in several included studies.
Conclusions: Meta-analysis found a higher diagnostic accuracy of ABVS in benign and malignant breast lesions. These results provide a reference for clinical practitioners in the selection of diagnostic methods, but considering the possible bias of the included studies, the results need to be treated with caution and further verified.
Keywords: Breast cancer; automated breast volume scanning (ABVS); hand-held ultrasound (HHUS); meta-analysis; molybdenum-target mammography.
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-24-135/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of an automated breast volume scanner compared with a hand-held ultrasound: a meta-analysis.Gland Surg. 2019 Dec;8(6):698-711. doi: 10.21037/gs.2019.11.18. Gland Surg. 2019. PMID: 32042678 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of combined use of automated breast volume scanning & hand-held ultrasound for breast lesions.Indian J Med Res. 2021 Aug;154(2):347-354. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_836_19. Indian J Med Res. 2021. PMID: 35295015 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of automated breast volume scanning and hand- held ultrasound in the detection of breast cancer: an analysis of 5,566 patient evaluations.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(21):9101-5. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.21.9101. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25422185
-
Automatic Breast Volume Scanner versus Handheld Ultrasound in Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Aug;45(8):1874-1881. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.04.028. Epub 2019 May 24. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31130410
-
Evaluation of Diagnostic Performance of Automatic Breast Volume Scanner Compared to Handheld Ultrasound on Different Breast Lesions: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Feb 19;12(2):541. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020541. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204629 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing Ultrasound as a Tool for Monitoring Tumor Regression During Chemotherapy: Insights from a Cohort of Breast Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 11;17(10):1626. doi: 10.3390/cancers17101626. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40427125 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
