On Levodopa Interactions with Brain Disease Amyloidogenic Proteins at the Nanoscale
- PMID: 40256523
- PMCID: PMC12004170
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01028
On Levodopa Interactions with Brain Disease Amyloidogenic Proteins at the Nanoscale
Abstract
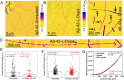
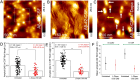
The cerebral accumulation of α-synuclein (α-Syn) and amyloid β-1-42 (Aβ-42) proteins is known to play a key role in the pathology of Parkinson's disease (PD). Currently, levodopa (L-dopa) is the first-line dopamine replacement therapy for treating bradykinetic symptoms (i.e., difficulty initiating physical movements), which become visible in PD patients. Using atomic force microscopy, we evidence at nanometer length scales the differential effects of L-dopa on the morphology of α-Syn and Aβ-42 protein fibrils. L-dopa treatment was observed to reduce the length and diameter of both types of protein fibrils, with a stark reduction mainly observed for Aβ-42 fibrils in physiological buffer solution and human cerebrospinal fluid. The insights gained on Aβ-42 fibril disassembly from the label-free nanoscale imaging experiments are substantiated by using atomic-scale molecular dynamics simulations. Our results indicate L-dopa-driven reversal of amyloidogenic protein aggregation, which might provide leads for designing chemical effector-mediated disassembly of insoluble protein aggregates.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nanoscale imaging of individual amyloid aggregates extracted from brains of Alzheimer and Parkinson patients reveals presence of lipids in α-synuclein but not in amyloid β1-42 fibrils.Protein Sci. 2023 Apr;32(4):e4598. doi: 10.1002/pro.4598. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36823759 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the Role of Lipids in the Aggregation of Amyloidogenic Proteins.Acc Chem Res. 2023 Nov 7;56(21):2898-2906. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00386. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Acc Chem Res. 2023. PMID: 37824095 Free PMC article.
-
Co-aggregation of pro-inflammatory S100A9 with α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: ex vivo and in vitro studies.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jun 4;15(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1210-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29866153 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule observation of self-propagating amyloid fibrils.Microscopy (Oxf). 2022 Jun 6;71(3):133-141. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfac011. Microscopy (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35253856 Review.
-
Elucidating the Structures of Amyloid Oligomers with Macrocyclic β-Hairpin Peptides: Insights into Alzheimer's Disease and Other Amyloid Diseases.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Mar 20;51(3):706-718. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00554. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29508987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhattacharya S.; Xu L.; Thompson D. Revisiting the earliest signatures of amyloidogenesis: Roadmaps emerging from computational modeling and experiment. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2018, 8 (4), e135910.1002/wcms.1359. - DOI
-
- Xu L.; Bhattacharya S.; Thompson D., Predictive Modeling of Neurotoxic α-Synuclein Polymorphs. In Computer Simulations of Aggregation of Proteins and Peptides; Springer US: New York, NY, 2022; 379–399.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
