Recycling Motorcycle Exhaust Soot into Fluorescent Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for Sensing Ferrocyanide Ions and Bioimaging Cells: A Method for Waste Utilization
- PMID: 40256545
- PMCID: PMC12004190
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00229
Recycling Motorcycle Exhaust Soot into Fluorescent Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for Sensing Ferrocyanide Ions and Bioimaging Cells: A Method for Waste Utilization
Abstract
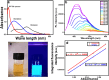
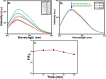
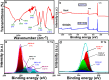
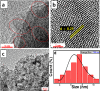
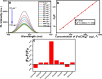
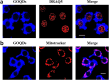
Graphene oxide quantum dots (GOQDs) with a high quantum yield (50%) were synthesized using soot collected from a motorcycle (petroleum vehicle) exhaust pipe and applied as sensors for ferrocyanide ([Fe(CN)6]4-) ions and as bioimaging agents in a cancer cell line. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data for the GOQDs revealed a C/O ratio of 2.49, which was close to that of graphene oxide (GO). The synthesized GOQDs exhibited strong blue fluorescence. High sensitivity to detect [Fe(CN)6]4- was reported in GOQDs with a detection limit of 0.46 nmol mL-1, and a strong linear relationship was achieved in the concentration range of 100-1100 μg L-1. The results demonstrate the utility of GOQDs for detecting [Fe(CN)6]4- in a real scenario. The GOQDs exhibited almost negligible cytotoxicity in cells and were internalized within 4 h of incubation, emitting blue fluorescence in the cytoplasm. This suggests that the GOQDs are promising bioimaging agents for biomedical applications. In general, these waste-derived GOQDs appear to be good chemo- and biosensing probes for real-life applications.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Preparation of graphene oxide quantum dots from waste toner, and their application to a fluorometric DNA hybridization assay.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jun 27;186(7):483. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3539-x. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31250112
-
Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 13;15(2):632. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020632. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839953 Free PMC article.
-
A strategy for preparing non-fluorescent graphene oxide quantum dots as fluorescence quenchers in quantitative real-time PCR.RSC Adv. 2020 Apr 16;10(25):14944-14952. doi: 10.1039/d0ra00142b. eCollection 2020 Apr 8. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35497124 Free PMC article.
-
Photoluminescence and Fluorescence Quenching of Graphene Oxide: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 17;12(14):2444. doi: 10.3390/nano12142444. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current trends in carbon-based quantum dots development from solid wastes and their applications.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Apr;30(16):45528-45554. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-25822-y. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36809626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Shafy H. I.; Mansour M. S. M. Solid Waste Issue: Sources, Composition, Disposal, Recycling, and Valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27 (4), 1275–1290. 10.1016/j.ejpe.2018.07.003. - DOI
-
- Chien C.-F.; Aviso K.; Tseng M.-L.; Fujii M.; Lim M. K. Solid Waste Management in Emerging Economies: Opportunities and Challenges for Reuse and Recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 172, 10567710.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105677. - DOI
-
- Pandiyan S.; Arumugam L.; Srirengan S. P.; Pitchan R.; Sevugan P.; Kannan K.; Pitchan G.; Hegde T. A.; Gandhirajan V. Biocompatible Carbon Quantum Dots Derived from Sugarcane Industrial Wastes for Effective Nonlinear Optical Behavior and Antimicrobial Activity Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5 (47), 30363–30372. 10.1021/acsomega.0c03290. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou J.; Sheng Z.; Han H.; Zou M.; Li C. Facile Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots Using Watermelon Peel as a Carbon Source. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66 (1), 222–224. 10.1016/j.matlet.2011.08.081. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
