Unveiling Indirect ELISA Test against Nucleoprotein of H9N2 Comparing With Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
- PMID: 40256573
- PMCID: PMC12004048
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.4.889
Unveiling Indirect ELISA Test against Nucleoprotein of H9N2 Comparing With Hemagglutination Inhibition Test
Abstract
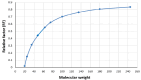
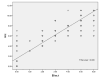
Influenza is an acute and highly contagious respiratory disease caused by an RNA virus belonging to the Orthomyxoviridae family. The virus has the capacity to infect both birds and mammals. Avian influenza is an infection or a syndrome caused by type A influenza viruses. The reservoir of this disease is defined as aquatic and migratory birds, and there is a possibility of this disease occurring in any region. Influenza can be transmitted through contact with contaminated surfaces. Some strains, such as the Asian H9N2 strain, have been observed to cause respiratory diseases in people in Asia. Therefore, this study aims to diagnose the disease in infected poultry with greater speed and ease by screening them with nucleoprotein of H9N2, thus preventing outbreaks. An indirect ELISA test was developed using the nucleoprotein of the H9N2 A/Chicken/Iran/259/2014 virus, with a molecular weight of 60 kilodaltons, which was separated from the virus by the electroelution method with the use of the monoclonal antibody against nucleoprotein serving as the standard. Subsequently, the results of the indirect ELISA test and the hemagglutination inhibition tests were compared using 300 serum samples from birds. The findings of this study illustrated the correlation between the indirect ELISA test and the hemagglutination inhibition test when analyzed together. A Spearman's correlation coefficient indicated that there was a significant and strong positive relationship between the two variables (ρ =0.901, p < .001, N = 300). The indirect ELISA test showed a sensitivity of 90% and a specificity of 92%. Since the disease with mild symptoms can make the diagnosis difficult, we need to control and quickly identify the avian influenza virus. Our indirect Elisa test could help detect a wide range of strains by utilizing a conserved antigen as well as being able to be used for screening more suspected samples in a time efficient manner as compared to the golden standard test, hemagglutination inhibition.
Keywords: Indirect ELISA TEST; Influenza; hemagglutination inhibition test; monoclonal antibody; nucleoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article have been reported.
Figures
References
-
- Katz JM, Veguilla V, Belser JA, Maines TR, Van Hoeven N, Pappas C, et al. The public health impact of avian influenza viruses. Poultry science. 2009;88(4):872–9. - PubMed
-
- Swayne DE. Diseases of poultry: John Wiley & Sons. 2013.
-
- OIE. Manual for diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals, Chapter 2.2. 4. Nosemosis of honey bees Office International des Epizooties, Paris, France. 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical