Evaluation of Indigenous Latex Agglutination Assay based on Recombinant Pasteurella Lipoprotein E (rPlpE) As Antigen for Detection of Anti Mannheimia Haemolytica - IgG Antibodies
- PMID: 40256586
- PMCID: PMC12004040
- DOI: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.4.848
Evaluation of Indigenous Latex Agglutination Assay based on Recombinant Pasteurella Lipoprotein E (rPlpE) As Antigen for Detection of Anti Mannheimia Haemolytica - IgG Antibodies
Abstract
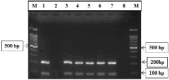
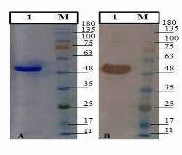
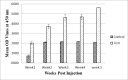
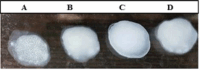
Mannheimia Haemolytica (M. haemolytica) is an organism causing pneumonia in ruminants. M. haemolytica causes severe economic losses to the global livestock industry. Several diagnostic methods have been developed, including bacterial culture, bacterial DNA detection and serological assays. Diagnosis of M. haemolytica is based on the bacteriological methods such as isolation of the microorganisms from clinical samples. Available methods are time consuming and not easy to perform. Serological tests based on recombinant proteins may provide higher sensitivity and specificity than culture tests. There is a need for new diagnostic methods to detect M. haemolytica -specific antibodies. In this study, a latex agglutination test (LAT) was developed based on recombinant outer membrane pasteurella lipoprotein E (rPlpE) for detecting specific antibodies against M. haemolytica. Expressed recombinant PlpE was coated with latex particles for a latex agglutination test. The recombinant PlpE was able to detect anti-M. haemolytica IgG in positive sera, but showed no immunoreaction with Pasteurella multocida and negative samples. These results suggest that the rPlpE can be used to detect the specific anti Mannheimia Haemolytica - IgG Antibodies. Because the recombinant proteins can be produced efficiently and are inexpensively, their use in diagnostic kits such as LATs as reagents can reduce the cost of them. This rapid and specific anti M. haemolytica antibody detection method using recombinant proteins can save cost and be widely applied for efficient and practical detection of. M. haemolytica.
Keywords: Antibody; Latex agglutination test; PlpE; Recombinant protein; Mannheimia Haemolytica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Quinn PJ, Markey BK, Leonard FC, Hartigan P, Fanning S, Patrick ESF. Veterinary Microbiology and Microbial Disease. 2nd ed. UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2011. p. 928.
-
- Yap KL. Development of a slide latex agglutination test for rotavirus antigen detection. Malaysian Journal of Pathology. 1994; 16:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Abdoel TH, Smits HL. Rapid latex agglutination test for the serodiagnosis of human brucellosis. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease. 2007;57:123–8. - PubMed
-
- Molina-Bolivar JA, Galisteo-Gonzalez F. Latex immunoagglutination assays. Polymer Reviews. 2005; 45:59–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
