Dentinal tubule penetration of a silicone-based endodontic sealer following N-acetyl cysteine intracanal medicament removal using ultrasonic agitation and laser activated irrigation - An in vitro study
- PMID: 40256695
- PMCID: PMC12007743
- DOI: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_842_24
Dentinal tubule penetration of a silicone-based endodontic sealer following N-acetyl cysteine intracanal medicament removal using ultrasonic agitation and laser activated irrigation - An in vitro study
Abstract
Context: The removal of intracanal medicament is essential for sealer penetration and the success of endodontic therapy.
Aims: To evaluate and compare the dentinal tubule penetration of a silicone-based endodontic sealer following N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) intracanal medicament removal using ultrasonic agitation and laser-activated irrigation.
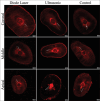
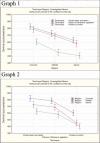
Materials and methods: Eighty-one extracted single-rooted mandibular premolars were decoronated and prepared with ProTaper Universal rotary files up to MAF F3. To prepare medicament, NAC powder was mixed with propylene glycol in the ratio of 1:1, placed using a size #30 Lentulospiral, and specimens stored in an incubator for 14 days. The specimens were then instrumented with #30 Hedström and divided into three groups according to final irrigant activation techniques: Group I: Diode laser activation, Group II: Passive Ultrasonic agitation, Group III: No agitation (positive control). Canals were obturated with GuttaFlow bioseal sealer mixed with 0.1% Rhodamine B dye and gutta-percha cones and incubated for 7 days. The specimens were sectioned horizontally to obtain 1 mm thick sections from 2, 5, and 8 mm from the apex. Sections were examined under Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope to measure the depth of sealer penetration (in µm).
Statistical analysis: One-way analysis of variance and Tukeys multiple post hoc test.
Results: The highest mean depth of penetration of 728.52 µm was seen with Group I, followed by Group II and least was seen in Group III.
Conclusions: Diode laser activation group was most effective in the removal of NAC intracanal medicament from all the three regions of the root canal.
Keywords: Confocal laser scanning microscope; N-acetyl cysteine; conventional syringe needle irrigation; diode laser activation; guttaFlow bioseal; passive ultrasonic agitation.
Copyright: © 2025 Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bystrom A, Claesson R, Sundqvist G. The antibacterial effect of camphorated paramonochlorophenol, camphorated phenol and calcium hydroxide in the treatment of infected root canals. Endod Dent Traumatol. 1985;1:170–5. - PubMed
-
- Stuart CH, Schwartz SA, Beeson TJ, Owatz CB. Enterococcus faecalis: Its role in root canal treatment failure and current concepts in retreatment. J Endod. 2006;32:93–8. - PubMed
-
- El-Feky MA, El-Rehewy MS, Hassan MA, Abolella HA, Abd El-Baky RM, Gad GF. Effect of ciprofloxacin and N-acetylcysteine on bacterial adherence and biofilm formation on ureteral stent surfaces. Pol J Microbiol. 2009;58:261–7. - PubMed
-
- Blank-Gonçalves LM, Nabeshima CK, Martins GH, Machado ME. Qualitative analysis of the removal of the smear layer in the apical third of curved roots: Conventional irrigation versus activation systems. J Endod. 2011;37:1268–71. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous