Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) potentially associated with residual feed intake in Qinchuan beef cattle by hypothalamus and duodenum RNA-Seq data
- PMID: 40256725
- PMCID: PMC12007499
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19270
Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) potentially associated with residual feed intake in Qinchuan beef cattle by hypothalamus and duodenum RNA-Seq data
Abstract
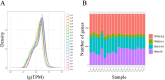
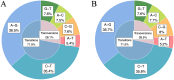
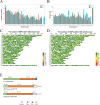
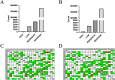
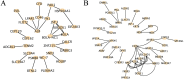
The regulation of residual feed intake (RFI) in beef cattle involves brain-gut mechanisms due to the interaction between neural signals in the brain and hunger or satiety in the gut. RNA-Seq data contain an extensive resource of untapped SNPs. Therefore, hypothalamic and duodenal tissues from ten extreme RFI individuals were collected, and transcriptome sequenced in this study. All the alignment data were combined according to RFI, and the SNPs in the same group were identified. A total of 270,410 SNPs were found in the high RFI group, and 255,120 SNPs were found in the low RFI group. Most SNPs were detected in the intronic region, followed by the intergenic region, and the exon region accounts for 1.11% and 1.38% in the high and low RFI groups, respectively. Prediction of high-impact SNPs and annotation of the genes in which they are located yielded 83 and 97 genes in the high-RFI and low-RFI groups, respectively. GO enrichment analysis of these genes revealed multiple NADH/NADPH-related pathways, with ND4, ND5, and ND6 significantly enriched as core subunits of NADH dehydrogenase (complex I), and is closely related to mitochondrial function. KEGG enrichment analysis of ND4, ND5, and ND6 genes was enriched in the thermogenic pathway. Multiple genes, such as ATP1A2, SLC9A4, and PLA2G5, were reported to be associated with RFI energy metabolism in the concurrent enrichment analysis. Protein-protein interaction analysis identified multiple potential candidate genes related to energy metabolism that were hypothesized to be potentially associated with the RFI phenotype. The results of this study will help to increase our understanding of identifying SNPs with significant genetic effects and their potential biological functions.
Keywords: Beef cattle; Duodenum; Hypothalamus; RNA-Seq; Single nucleotide polymorphisms.
© 2025 Su et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Cong-Jun Li is an Academic Editor for PeerJ.
Figures

References
-
- Archer JA, Bergh L. Duration of performance tests for growth rate, feed intake and feed efficiency in four biological types of beef cattle. Livestock Production Science. 2000;65(1–2):47–55. doi: 10.1016/S0301-6226(99)00181-5. - DOI
-
- Arthur PF, Archer JA, Johnston DJ, Herd RM, Richardson EC, Parnell PF. Genetic and phenotypic variance and covariance components for feed intake, feed efficiency, and other postweaning traits in Angus cattle. Journal of Animal Science. 2001;79(11):2805–2811. doi: 10.2527/2001.79112805x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

