Accurate and Efficient Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using Multi-Dimensional Features of Plasma Cell-Free DNA
- PMID: 40256837
- PMCID: PMC12338027
- DOI: 10.1002/hed.28154
Accurate and Efficient Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Using Multi-Dimensional Features of Plasma Cell-Free DNA
Abstract
Background: The incidence of Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is rising in recent years, especially in some non-developed parts of the world. Hence, cost-efficient means for sensitive detection of NPC are vital.
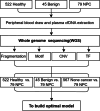
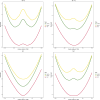
Methods: We recruited 646 participants, including healthy individuals, patients with benign nasopharyngeal diseases, and NPC patients for plasma cell-free DNA(cfDNA), which underwent low-depth whole-genome sequencing (WGS) to extract multi-dimensional molecular features, including fragmentation pattern, end motif, copy number variation(CNV), and transcription factors(TF). Based on these features, we employed a machine learning algorithm to build prediction models for NPC detection.
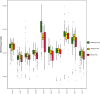
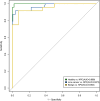
Results: We achieved a sensitivity of 95.8% and a specificity of 99.4% to discriminate NPC patients from healthy individuals.
Conclusions: This study can be a proof-of-concept for these multi-dimensional molecular features to be implemented as a noninvasive approach for the detection and even early detection of NPC.
Keywords: cell‐free DNA; copy number variations (CNV); machine learning; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; whole genome sequencing (WGS).
© 2025 The Author(s). Head & Neck published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can a Liquid Biopsy Detect Circulating Tumor DNA With Low-passage Whole-genome Sequencing in Patients With a Sarcoma? A Pilot Evaluation.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jan 1;483(1):39-48. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003161. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 38905450
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma detected noninvasively in the real world using three gene methylation analyses from automatically processed bilateral nasal swab samples.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):1147. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14508-y. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40618071 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of circulating cell-free DNA signatures for nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection.EBioMedicine. 2024 Oct;108:105321. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105321. Epub 2024 Sep 11. EBioMedicine. 2024. PMID: 39265506 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of sample site and collection procedure on identification of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):CD014780. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014780. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39679851 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre L. A., Bray F., Siegel R. L., Ferlay J., Lortet‐Tieulent J., and Jemal A., “Global Cancer Statistics, 2012,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 65 (2015): 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Su Z. Y., Siak P. Y., Lwin Y. Y., and Cheah S. C., “Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Current Insights and Future Outlook,” Cancer Metastasis Reviews 43 (2024): 919–939. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.‐P., Chan A. T. C., Le Q.‐T., Blanchard P., Sun Y., and Ma J., “Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma,” Lancet 394 (2019): 64–80. - PubMed
-
- Li T., Li F., Guo X., et al., “Anti‐EBV BNLF2b for Mass Screening for Nasopharyngeal Cancer,” New England Journal of Medicine 389, no. 9 (2023): 808–819. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RFCS20210701002/Shenzhen Rapha Biotechnology Incorporate R&D Clinical Study Fund
- KCXFZ20200201101050887/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- JCYJ20230807141514029/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- ZDSYS2019-0902092855097/Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission
- SZSM2022-11036/Shenzhen San-Ming Project of Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

