Efficient gene transfer by pulse parameters for electrochemotherapy of cells in vitro and in muscle and melanoma tumors in mice
- PMID: 40256892
- PMCID: PMC12182922
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2025-0027
Efficient gene transfer by pulse parameters for electrochemotherapy of cells in vitro and in muscle and melanoma tumors in mice
Abstract
Background: In recent years, various gene therapy strategies have been developed for cancer treatment. One of these strategies is electroporation-based delivery of therapeutic transgenes - gene electrotransfer (GET). Electrochemotherapy and GET have been combined in several contemporary preclinical and veterinary studies. In most cases, two different pulse protocols are used, each for a specific treatment. The aim of our current study was to test whether the standard pulse protocol used in daily clinical practice for electrochemotherapy can also be used for effective GET.
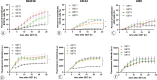
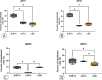
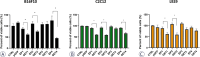
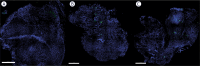
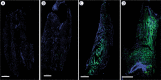
Materials and methods: Experiments were performed in vitro in a tumor (B16F10) and two normal tissue cell lines (C2C12 myoblasts and L929 fibroblasts). Four different GET protocols, three using monopolar electric pulses and one bipolar electric pulses, were tested for the GET of plasmid DNA, which codes for green fluorescent protein in vitro. In addition, two GET protocols were chosen for in vivo tumor and muscle transfection.
Results: Two GET protocols using monopolar electric pulses of different voltages delivered at 1 Hz transfected B16F10 tumor cells significantly better than normal cells. GET4 protocol, which uses monopolar electric pulses at 5 kHz, again transfected the B16F10 tumor cells significantly better, but the difference to the C2C12 myoblast cells was not significant. Compared with other GET protocols, GET3 using bipolar electric pulses at 1 Hz was significantly less effective. Both the GET2 (1 Hz) and GET4 (5 kHz) protocols resulted in similar tumor transfection efficiencies, whereas only the GET4 protocol was effective for muscle transfection in vivo.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated the efficient transfection of tumors and muscles with the GET4 pulse protocol, which is used clinically for electrochemotherapy. The use of this protocol could enable simultaneous electrochemotherapy and GET of the therapeutic gene in one session, which will significantly shorten the procedure and thus will be more tolerable for patients.
Keywords: cells; electrochemotherapy; gene electrotransfer; muscle; tumor.
© 2025 Masa Omerzel et al., published by Sciendo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
