Pathogenetic Involvement of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
- PMID: 40257374
- PMCID: PMC12010764
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.70455
Pathogenetic Involvement of Autophagy and Mitophagy in Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
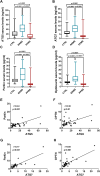
Primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) affects a subset of MS patients and is characterised by continuous progression from the onset. The molecular mechanisms underlying PPMS are poorly understood, and therapeutic options are limited, with no specific markers for early detection and monitoring. This study investigated the roles of autophagy and mitophagy in PPMS. We found that autophagy markers (ATG5 and ATG7) and mitophagy markers (Parkin and Optineurin) were significantly reduced in the serum of PPMS patients compared to control and relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS) individuals. This reduction was associated with an increase in markers indicative of neurodegeneration and mitochondrial dysfunction. Additionally, a positive correlation between autophagy and mitophagy proteins in the PPMS group suggests that these mechanisms are reciprocally associated and modulated in PPMS. Our investigation reveals that autophagy and mitophagy are actively involved in PPMS and exhibit distinct patterns across MS subtypes. Measurements of circulating components related to autophagy and mitophagy could serve as potential biomarkers for early PPMS detection.
Keywords: ATG5; ATG7; GFAP; Optineurin; Parkin; biomarker; lactate; serum.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Permission to reproduce material from other sources: The authors have nothing to report.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GJC23065A/Fondazione Telethon
- 2022PX3SR3/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- P2022A35RA_001/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- 2020RRJP5L/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- 202259LHXM/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- P2022WY85K_001/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PNRR-MCNT1-2023-12378355/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- CN00000041/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- PRIN20227Z2XRB/Ministero dell'Università e della Ricerca
- cod.2022/R-Multi/050/Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla
- IG-19803/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- IG-23670/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- MFAG-29087/Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro
- 853057/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- UMO-2021/43/I/NZ3/00510/Narodowe Centrum Nauki
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

