Dynamical analysis of scabies delayed epidemic model with second-order global stability
- PMID: 40258081
- PMCID: PMC12011307
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319095
Dynamical analysis of scabies delayed epidemic model with second-order global stability
Abstract
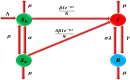
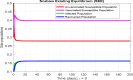
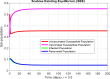
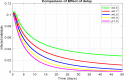
Scabies is a highly transmitted skin disease that can affect people of all ages, especially children. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa are the regions most affected. For the study of the dynamics of scabies in the population, the mathematical model is designed with delay differential equations (DDEs) for four subpopulations: unvaccinated individuals, vaccinated individuals, infected individuals, and recovered individuals. The fundamental properties of the model, such as positivity, boundedness, existence, and uniqueness, are proved. The equilibria, reproduction number, sensitivity analysis, and (Local and Global) stabilities for the second order are studied rigorously. The numerical simulations were performed to confirm the validity of their theoretical results. The study's findings suggest delay-based modeling of scabies and the advanced stability analysis provides a better understanding of epidemic management and disease dynamics over time.
Copyright: © 2025 Fadhal et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modeling the transmission dynamics of delayed pneumonia-like diseases with a sensitivity of parameters.Adv Differ Equ. 2021;2021(1):468. doi: 10.1186/s13662-021-03618-z. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Adv Differ Equ. 2021. PMID: 34691162 Free PMC article.
-
A SEIR model with memory effects for the propagation of Ebola-like infections and its dynamically consistent approximation.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021 Sep;209:106322. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106322. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2021. PMID: 34390936
-
Stochastic delayed analysis of coronavirus model through efficient computational method.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 10;14(1):21170. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70089-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39256433 Free PMC article.
-
Scabies: an epidemiologic reassessment.Ann Intern Med. 1983 Apr;98(4):498-503. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-98-4-498. Ann Intern Med. 1983. PMID: 6340578 Review.
-
[Causes of spread and return of scabies in health care institutes; literature analysis of 44 epidemics].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1998 Feb 14;142(7):354-7. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1998. PMID: 9562741 Review. Dutch.
References
-
- Bhunu CP, Mushayabasa S, Monera TG. Assessing the impact of vaccination on controlling the spread of human scabies. ISRN Comput Biol. 2013;2013:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2013/362973 - DOI
-
- Rashid S, Kanwal B, Jarad F, Elagan SK. A peculiar application of the fractal–fractional derivative in the dynamics of a nonlinear scabies model. Results Physics. 2022;38:105634. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2022.105634 - DOI
-
- Mhlanga A, Mupedza TV, Mazikana TM. Optimal control and cost-effective analysis of a scabies model with direct and indirect transmissions. J Biol Syst. 2022;30(02):261–83. doi: 10.1142/s0218339022500097 - DOI
-
- Browne E, Driessen MM, Cross PC, Escobar LE, Foley J, López-Olvera JR, et al.. Sustaining transmission in different host species: the emblematic case of sarcoptes scabiei. BioScience. 2021;72(2):166–76. doi: 10.1093/biosci/biab106 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

