Global maternal mortality associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40258634
- PMCID: PMC12015698
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2024-015815
Global maternal mortality associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Pregnant and recently pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 are at increased risk of death and serious complications than those without the infection. The extent of variation in mortality rates in pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection across regions, and the causes of death are not known. We systematically reviewed all available evidence on the variation in mortality rates in pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection across geographical and country income groups, and the reported cause of death.
Methods: We searched major databases (December 2019-January 2023) including Medline, LILACS, BIREME and Embase. We included studies that reported deaths in at least 10 consecutive pregnant or recently pregnant women with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and assessed the studies' risk of bias. We calculated the summary estimates of any cause of death as proportions with 95% CIs using a multilevel random-effects logistic regression model. Subgroup analyses were performed by geographical region and country income groups. We used International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems-Maternal Mortality to categorise the reported cause of death.
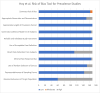
Findings: From 1 326 315 citations, we included 169 studies (319 172 women with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection; 4253 women died). The overall rate of unspecified maternal death was 0.87% (95% CI 0.64% to 1.16%). There were significant differences between geographical regions in rates of maternal mortality, with the highest rates in Sub-Saharan Africa (3.48%; 95% CI 0.66% to 16.42%) and Latin America and the Caribbean (3.16%, 95% CI 1.53% to 6.43%). Rates of maternal mortality varied by country income groups, with the highest rates in low-income countries (4.66%, 95% CI 0.75% to 24.07%). Among women with reported cause of death, 98.6% (2,390/2,423) of deaths were attributable to COVID-19.
Interpretation: Rates of deaths in pregnant and recently pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection vary significantly across regions and by country income groups, with the highest burden in Sub-Saharan Africa and low-income countries. COVID-19 is the main reported cause of death.
Prospero registration number: CRD42020224120.
Keywords: Maternal health; SARS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Trends in maternal mortality 2000 to 2020: estimates by WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, World Bank Group and UNDESA/Population Division. Geneva: 2023.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
