The causal relationship between six mental disorders and breast cancer risk: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 40258734
- PMCID: PMC12014078
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042209
The causal relationship between six mental disorders and breast cancer risk: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
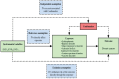
Psychological disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder (BD), major depressive disorder (MDD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and anxiety disorder (AD) are widespread. Mendelian randomization (MR) was used in this study in order to investigate possible causal relationships between psychiatric disorders and breast cancer (BC). We employed publicly accessible summary statistics from extensive genome-wide association studies to identify, perform quality control, and cluster genetic variant loci linked to schizophrenia, ADHD, MDD, ASD, BD, AD, and BC as instrumental variables. The MR analysis utilized inverse variance weighting, MR-Egger regression, and weighted median estimation to assess the causal links between psychiatric disorders and BC. Additionally, heterogeneity and sensitivity tests were conducted to ensure the robustness of inverse variance weighting results. According to the results of the two-sample MR analysis, schizophrenia, BD, MDD, ADHD, ASD are not causally linked to BC. According to the results of the two-sample MR analysis, schizophrenia, BD, MDD, ADHD, ASD are not causally linked to BC. But there is a causal relationship between AD and BC. The MR analysis showed no evidence of a causal relationship between schizophrenia, BD, MDD, ADHD, ASD, and BC risk. However, research found a genetic causal relationship between AD and BC, and it is positively correlated.
Keywords: Mendelian randomization schizophrenia; bipolar disorder; breast cancer; psychological disorders.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Causal associations between immune cells and psychiatric disorders: a bidirectional mendelian randomization analysis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8909-8922. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03818-4. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39878811
-
Causal relationship between attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and atherosclerosis: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 27;104(26):e42859. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042859. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40587750 Free PMC article.
-
Causal relationship between psychiatric disorders and sensorineural hearing loss: A bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization analysis.J Psychosom Res. 2024 Apr;179:111641. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2024.111641. Epub 2024 Mar 7. J Psychosom Res. 2024. PMID: 38461621
-
Pharmacological intervention for irritability, aggression, and self-injury in autism spectrum disorder (ASD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 9;10(10):CD011769. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011769.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37811711 Free PMC article.
-
Methylphenidate for children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorder.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 21;11(11):CD011144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29159857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gandhi L, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, et al. . Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:2078–92. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Colditz GA, Rosner B. Cumulative risk of breast cancer to age 70 years according to risk factor status: data from the Nurses’ Health Study. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;152:950–64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical