Kinetic modeling and CFD simulation of in-situ heavy oil upgrading using batch reactors and porous media
- PMID: 40258906
- PMCID: PMC12012214
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98494-y
Kinetic modeling and CFD simulation of in-situ heavy oil upgrading using batch reactors and porous media
Abstract
The depletion of conventional oil reserves and rising global energy demand necessitate efficient extraction methods for unconventional resources like heavy oil. This study successfully applies the coupling of chemical reaction kinetics with fluid dynamics in porous media for in-situ heavy oil upgrading, extending existing models to dynamic conditions. Using advanced kinetic modeling and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), catalytic reactions are analyzed employing a Ni-W-Mo catalyst. The primary aim of this study is to investigate the effects of temperature, oil composition, and residence time on the upgrading process and the resulting product distribution. Simulations were first performed in a non-porous batch reactor to identify optimal reaction conditions, followed by modeling reactive flow in porous media to better simulate real-world reservoir conditions. The results show that temperature and residence time significantly influence conversion rates and product yields, with a 30% increase in lighter hydrocarbon production as the reaction temperature is raised from 575 to 700 K. These findings emphasize the importance of dynamic modeling in optimizing in-situ upgrading processes and provide insights into improving unconventional oil recovery techniques. This research provides a comprehensive framework to enhance the understanding of complex chemical and hydrodynamic interactions in porous media, contributing to the development of more effective oil recovery strategies for unconventional resources.
Keywords: Catalysts; Enhanced oil recovery (EOR); Heavy oil; In-situ upgrading; Porous media; Reaction kinetic.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





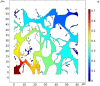
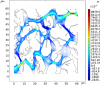
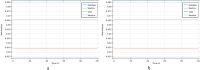

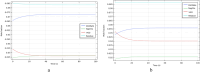







References
-
- Brozynski, M. T. & Leibowicz, B. D. Decarbonizing power and transportation at the urban scale: An analysis of the Austin, Texas Community Climate Plan. Sustain. Cities Soc.43, 41–54 (2018).
-
- Canton, H. International energy agency—IEA. In The Europa Directory of International Organizations 2021 684–686 (Routledge, 2021).
-
- Al-Marshed, A. et al. Optimization of heavy oil upgrading using dispersed nanoparticulate iron oxide as a catalyst. Energy Fuels29(10), 6306–6316 (2015).
-
- Muraza, O. & Galadima, A. Aquathermolysis of heavy oil: A review and perspective on catalyst development. Fuel157, 219–231 (2015).
-
- Perez-Perez, A. et al. Simulations of in-situ upgrading process: Interpretation of laboratory experiments and study of field-scale test. SPE J.24(06), 2711–2730 (2019).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

