Phytochemical analysis and biological study on Sinapis alba L. seeds extract incorporated with metal nanoparticles, in vitro approach
- PMID: 40258907
- PMCID: PMC12012182
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-95347-6
Phytochemical analysis and biological study on Sinapis alba L. seeds extract incorporated with metal nanoparticles, in vitro approach
Abstract
White mustard (Sinapis alba L.) seeds are the most commonly used mustard species in herbal medicine to treat a wide range of inflammatory disorders. Due to its increased bioavailability and lower toxicity, the green biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles (M-NPs) utilizing plant extract as a capping agent has been demonstrated over a number of years. Thus, the current study sought to examine the in vitro biological activity of copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) and selenium nanoparticles (Se-NPs) that were biosynthesized using aqueous, methanolic, and petroleum ether extracts from S. alba seeds. Phytochemical and in vitro biological activities (antioxidant, scavenging, anti-diabetic, anti-acetylcholinesterase, anti-arthritic, anti-inflammatory, and cytotoxic activities) were assayed in all prepared extracts before and after being used for the biosynthesis of the M-NPs. It was found that the total methanolic extract possessed the highest biological activities compared to other native extracts. The LC-ESI-MS/MS analysis of secondary metabolites showed that the total methanolic extract contained 7 phenolic acids and 9 flavonoid aglycones. This helped find the active ingredients. We characterized 8 phenolic acid derivatives, 7 flavonoid glycosides, 4 aliphatic glucosinolates, and 3 aromatic aryl glucosinolates in the aqueous extract. Furthermore, the methanolic extract contains the highest concentrations of total polyphenols, condensed tannins, and total flavonoid compounds. The biosynthesized Se-NPs using methanolic extract showed higher in vitro biological activities compared to those of the biosynthesized CuO-NPs. The median lethal dose (LD50) showed that the biosynthesized Se-NPs using the studied extracts appeared safer compared to those of the biosynthesized CuO-NPs. The findings of this study concluded that the total methanolic extract is the most suitable bioresource for biosynthesizing Se-NPs through green nanotechnology, with higher biological efficiency in relation to its metabolite fingerprint.
Keywords: Sinapis alba L.; Anti-diabetic Activity; Cytotoxic Activity; Green Nanotechnology; Metal Nanoparticles; Seeds.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical statements: The experimental design related to the assays on human normal and cancer cells, as well as the experiment carried out on the experimental animals, followed the methodology reported in the “Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals” and was authorized by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee of the National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, Egypt, under the number 13020243.
Figures


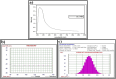
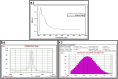
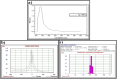
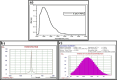
Similar articles
-
In Vitro Study on Effect of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on the Biological Activities of Croton tiglium L. Seeds Extracts.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Aug 1;23(8):2671-2686. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.8.2671. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36037121 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite Profiling and Biological Activity Assessment of Casuarina equisetifolia Bark after Incorporating Gold Nanoparticles.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022 Oct 1;23(10):3457-3471. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.10.3457. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2022. PMID: 36308372 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus Leaf Extract and its impact on germination and Phytochemical composition of Lactuca sativa.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 4;14(1):30203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78956-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39632890 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical investigation, in vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of aqueous and organic extracts of toxic plant: Atractylis gummifera L.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 10;253:112640. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112640. Epub 2020 Feb 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32027998 Review.
-
New frontiers in the plant extract mediated biosynthesis of copper oxide (CuO) nanoparticles and their potential applications: A review.Environ Res. 2022 Jan;203:111858. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111858. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 34389352 Review.
References
-
- Falzon, C. C., Balabanova, A. & Phytotherapy An introduction to herbal medicine. Prim. Care44 (2), 217–227 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Chaachouay, N. & Zidane, L. Plant-derived natural products: A source for drug discovery and development. Drugs Drug Candidat.3 (1), 184–207 (2024).
-
- Grygier, A. Mustard seeds as a bioactive component of food. Food Rev. Int.39 (7), 4088–4101 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

