Spatial regulation of chrysosplenetin on amino acid homeostasis linked to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium berghei K173 based on targeted metabolomics
- PMID: 40258976
- PMCID: PMC12012018
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-98409-x
Spatial regulation of chrysosplenetin on amino acid homeostasis linked to artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium berghei K173 based on targeted metabolomics
Abstract
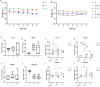
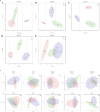
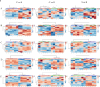
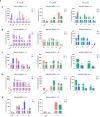
Chrysosplenetin, a polymethoxy flavonol purified in our laboratory from the waste products generated during the industrial extraction of artemisinin, has been previously demonstrated to be a potential inhibitor of artemisinin resistance. Based on NMR-untargeted metabolomics, one of its hypothesized mechanisms of action is associated with the regulation of amino acid metabolism. In this study, we further quantified the key amino acids using LC-MS/MS targeted metabolomics and screened out the perturbed metabolic pathway network, which was characterized by tissue-specific differences. As a result, among the commonly and uniquely altered metabolites, increased levels of phenylalanine, tryptophan, and isoleucine were detected in the serum and various organs of the resistant groups. Interestingly, while the individual use of chrysosplenetin or artemisinin elevated the contents of these amino acids, their combination led to a significant down-regulation of these amino acids in the serum and intestines. Therefore, chrysosplenetin has the potential to act as a restorer of amino acid metabolism homeostasis, which is associated with artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium berghei K173.
Keywords: Amino acids; Artemisinin resistance; Chrysosplenetin; LC-MS/MS based targeted metabolomics; TMAO.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: The protocol was submitted to and approved by the University Ethics Committee (YXYLL-2021-10). Animal experiment: All experiment animals adhere to the ARRIVE guidelines.
Figures




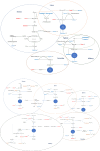
References
-
- WHO. World malaria report 2020: 20 years of global progress and challenges. (2020). http://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme
-
- WHO. Word malaria report 2021. (2021). https://www.who.int/teams/global-malaria-programme/reports/world-malaria...
-
- Duffy, P. E. & Sibley, C. H. Are we losing artemisinin combination therapy already? Lancet366, 1908–1909. 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67768-9 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

