Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide inhibits NSCLC proliferation and immune evasion via FXR1-IL-35 axis signaling pathway
- PMID: 40259042
- PMCID: PMC12228671
- DOI: 10.1007/s11418-025-01894-7
Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide inhibits NSCLC proliferation and immune evasion via FXR1-IL-35 axis signaling pathway
Abstract
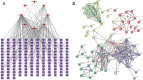
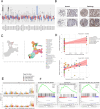
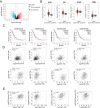
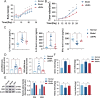
Dendrobium huoshanense has received special attention for its advantages in the treatment of lung cancer, but the underlying molecular mechanisms are not yet well understood. First, we obtained 8 active ingredients and 159 effective action targets of Dendrobium huoshanense using network pharmacology, and searching target interactions through STRING, constructing the PPI network and KEGG, GO and Hallmark enrichment analysis. Then, we combined target's enrichment analysis and GSEA enrichment analysis of IL-35, indicating the mechanism of cDHPs for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) may be related to tight junction and NSCLC pathway. Further, FXR1 and ACTR3 were identified as core therapeutic targets, and high expression of FXR1 or ACTR3 was significantly associated with poor prognosis of patients. The analysis of single-cell data also indicated that the percentage of CD4-CTLA4-Treg cells may be increased by the expression of IL-35, resulting in a suppressive immune microenvironment. Next, In vivo experiment, we detected iTr35 by flow cytometry, detected IL-35 level by RT-PCR, Western blotting and ELISA, and detected NK cell activity to explore the immunomodulatory effects and anti-tumor mechanism of cDHPs. After cDHPs administration, the conversion of CD4+ T cells to iTr35 is inhibited, p35 and EBI3 in both protein and mRNA levels, the levels of IL-35 and IL-4 in serum decreased. The levels of IFN-γ, while the activity of NK cells in mice increased, enhancing the anti-tumor immune effect of the organism. Finally, analysis of sequencing data from the immunotherapy cohort of tumor-bearing mice obtained from the TISMO database shows that the combination of cDHPs and PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies improves effector and thus PD-1/PD-L1 antibody efficacy. These findings suggest that cDHPs inhibit NSCLC proliferation and immune escape via the FXR1-IL-35 axis signaling pathway.
Keywords: IL-35; Immune evasion; Tumor microenvironment; iTr35.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Ethical protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Wannan Medical College (LLSC-2021-199). Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

