Multi-omic and spatial analysis of mouse kidneys highlights sex-specific differences in gene regulation across the lifespan
- PMID: 40259083
- PMCID: PMC12081296
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02161-x
Multi-omic and spatial analysis of mouse kidneys highlights sex-specific differences in gene regulation across the lifespan
Abstract
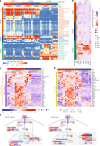
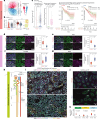
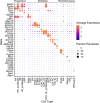
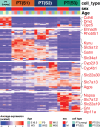
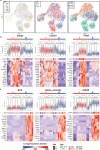
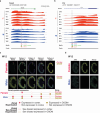
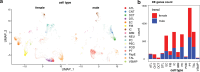
There is a sex bias in the incidence and progression of many kidney diseases. To better understand such sexual dimorphism, we integrated data from six platforms, characterizing 76 kidney samples from 68 mice at six developmental and adult time points, creating a molecular atlas of the mouse kidney across the lifespan for both sexes. We show that proximal tubules have the most sex-biased differentially expressed genes emerging after 3 weeks of age and are associated with hormonal regulations. We reveal potential mechanisms involving both direct and indirect regulation by androgens and estrogens. Spatial profiling identifies distinct sex-biased spatial patterns in the cortex and outer stripe of the outer medulla. Additionally, older mice exhibit more aging-related gene alterations in loops of Henle, proximal tubules and collecting ducts in a sex-dependent manner. Our results enhance the understanding of spatially resolved gene expression and hormone regulation underlying kidney sexual dimorphism across the lifespan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 AG075934/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK131377/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK3380/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U54AG075934/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01 DK131380/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

