Energy Metabolism and Brain Aging: Strategies to Delay Neuronal Degeneration
- PMID: 40259102
- PMCID: PMC12011708
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-025-01555-z
Energy Metabolism and Brain Aging: Strategies to Delay Neuronal Degeneration
Abstract
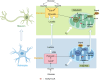
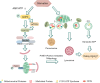
Aging is characterized by a gradual decline in physiological functions, with brain aging being a major risk factor for numerous neurodegenerative diseases. Given the brain's high energy demands, maintaining an adequate ATP supply is crucial for its proper function. However, with advancing age, mitochondria dysfunction and a deteriorating energy metabolism lead to reduced overall energy production and impaired mitochondrial quality control (MQC). As a result, promoting healthy aging has become a key focus in contemporary research. This review examines the relationship between energy metabolism and brain aging, highlighting the connection between MQC and energy metabolism, and proposes strategies to delay brain aging by targeting energy metabolism.
Keywords: Brain aging; Energy metabolism; Mitochondrial quality control; Neurons.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteotoxicity and mitochondrial dynamics in aging diabetic brain.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104948. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104948. Epub 2020 May 22. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32450345 Review.
-
Mitostasis in age-associated neurodegeneration.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Jan;1871(1):167547. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167547. Epub 2024 Oct 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025. PMID: 39437856 Review.
-
Mitochondrial Supercomplexes: Physiological Organization and Dysregulation in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 11;11:600. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00600. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33042002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Does impairment of energy metabolism result in excitotoxic neuronal death in neurodegenerative illnesses?Ann Neurol. 1992 Feb;31(2):119-30. doi: 10.1002/ana.410310202. Ann Neurol. 1992. PMID: 1349466 Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying perturbed energy metabolism and neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;893:154-75. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07824.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10672236 Review.
References
-
- Aman Y (2023) Isoleucine dietary restriction boosts healthspan and longevity in mice. Nat Aging 3(12):1471. 10.1038/s43587-023-00547-2 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C2024405023/Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
- C20190175/a scholarship from the Hebei Province, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

