Current progress and remaining challenges of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs): next generation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)?
- PMID: 40259322
- PMCID: PMC12013038
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-025-03277-2
Current progress and remaining challenges of peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs): next generation of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs)?
Abstract
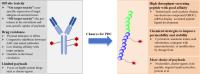
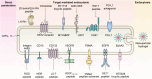
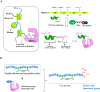
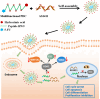
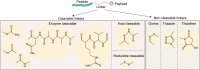
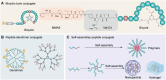
Drug conjugates have emerged as a promising alternative delivery system designed to deliver an ultra-toxic payload directly to the target cancer cells, maximizing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing toxicity. Among these, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) have garnered significant attention from both academia and industry due to their great potential for cancer therapy. However, peptide-drug conjugates (PDCs) offer several advantages over ADCs, including more accessible industrial synthesis, versatile functionalization, high tissue penetration, and rapid clearance with low immunotoxicity. These factors position PDCs as up-and-coming drug candidates for future cancer therapy. Despite their potential, PDCs face challenges such as poor pharmacokinetic properties and low bioactivity, which hinder their clinical development. How to design PDCs to meet clinical needs is a big challenge and urgent to resolve. In this review, we first carefully analyzed the general consideration of successful PDC design learning from ADCs. Then, we summarised the basic functions of each component of a PDC construct, comprising of peptides, linkers and payloads. The peptides in PDCs were categorized into three types: tumor targeting peptides, cell penetrating peptide and self-assembling peptide. We then analyzed the potential of these peptides for drug delivery, such as overcoming drug resistance, controlling drug release and improving therapeutic efficacy with reduced non-specific toxicity. To better understand the potential druggability of PDCs, we discussed the pharmacokinetics of PDCs and also briefly introduced the current PDCs in clinical trials. Lastly, we discussed the future perspectives for the successful development of an oncology PDC. This review aimed to provide useful information for better construction of PDCs in future clinical applications.
Keywords: Antibody drug conjugate; Clinical trials; Peptide drug conjugate; Pharmacokinetics; Targeted drug delivery.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics and consent to publish: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Ghosh S, Lai JY. An insight into the dual role of MoS2-based nanocarriers in anticancer drug delivery and therapy. Acta Biomater. 2024;179:36–60. - PubMed
-
- Yang Y, Wang S, Ma P, Jiang Y, Cheng K, Yu Y, Jiang N, Miao H, Tang Q, Liu F, Zha Y, Li N. Drug conjugate-based anticancer therapy - Current status and perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2023;552:215969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

