Curcumin prevents dexamethasone-induced activation of the pseudorabies virus in rat pheochromocytoma cells through the miR-155-5p-Aak1-Numb/Notch2 signalling axis
- PMID: 40259414
- PMCID: PMC12010530
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-025-01509-9
Curcumin prevents dexamethasone-induced activation of the pseudorabies virus in rat pheochromocytoma cells through the miR-155-5p-Aak1-Numb/Notch2 signalling axis
Abstract
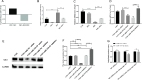
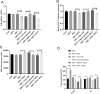
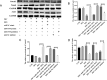
Pseudorabies virus (PRV) causes neurological disorders and organ damage in diseased animals. After initial infection, PRV activity is gradually inhibited; however, stress stimulation increases the host's glucocorticoid levels, which overcomes the inhibition of PRV activity. Curcumin (Cur) helps maintain the inhibitory state of the Epstein-Barr virus, although further research is needed to establish whether Cur can prevent PRV activation triggered by stress hormones. In this study, we used PC-12 cells to determine the effects of Cur on PRV activation. The cells were successfully infected with PRV at a multiplicity of infection of 1 for 24 h, resulting in the inhibition of PRV activity. Following incubation with 0.5 µM dexamethasone (DEX) for 4 h, the inhibition of PRV activity was blocked. Further mechanistic analyses using a dual-luciferase assay revealed that miR-155-5p directly targets and regulates Aak1 and its downstream signalling molecules, Numb and Notch2, in maintaining and disrupting PRV inhibition. Moreover, in vitro experiments using miR-155-5p mimics and inhibitors, combined with Aak1 overexpression and interference, confirmed that the miR-155-5p-Aak1-Numb/Notch2 axis prevented DEX-induced disruption of PRV inhibition by Cur. These findings provide a novel regulatory target for preventing stress-activated PRV and provide evidence for the potential use of Cur as a stress modulator in practical applications.
Keywords: DEX; curcumin; miR-155-5p/Aak1; pseudorabies virus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Wang HH, Liu J, Li LT, Chen HC, Zhang WP, Liu ZF (2020) Typical gene expression profile of pseudorabies virus reactivation from latency in swine trigeminal ganglion. J Neurovirol 26:687–695 - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, Liu Y, Yang F, Liu Y, Wang N, Li Y, Liu Y, Qiu Z, Zhang L, You X, Gan L (2024) MicroRNA-194-5p/heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor signaling mediates dexamethasone-induced activation of pseudorabies virus in rat pheochromocytoma cells. Vet Microbiol 290:109974 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

