Cholesterol-Rich Antibiotic-Loaded Liposomes as Efficient Antimicrobial Therapeutics
- PMID: 40259917
- PMCID: PMC12011041
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S513553
Cholesterol-Rich Antibiotic-Loaded Liposomes as Efficient Antimicrobial Therapeutics
Abstract
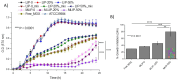
Introduction: Liposomal antibiotics have demonstrated higher bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities than free drugs. In this study, we investigated the effects of cholesterol (Chol) content of liposomes, liposome concentration, and surface coating with polyethylene glycol (PEG) on the antimicrobial activity of moxifloxacin (MOX) liposomes against Staphylococcus epidermidis (ATCC 35984) (S.e).
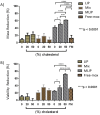
Methods: MOX-liposome compositions with increasing Chol content were evaluated for their susceptibility to planktonic S.e (growth inhibition, killing, and live-dead staining), as well as against pre-formed biofilms (crystal violet, MTT assay, and confocal microscopy). The MOX-liposomes prepared by active loading were characterized in terms of loading, size distribution, and zeta potential.
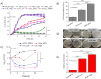
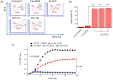
Results-discussion: All liposomes had nano-dimensions ranging in diameter from 92nm to 114nm, with zeta-potential values from -2.30mV to -4.50mV. Planktonic bacteria and established biofilms are significantly more susceptible to MOX-liposomes with higher Chol-content than other liposome-types, and the same MOX dose encapsulated in 10 times higher lipids demonstrated higher antimicrobial activity. Coating the MOX liposomes with PEG did not affect their activity. Flow cytometry showed higher binding of Chol-rich liposomes to bacteria, explaining the higher antimicrobial activity. Interestingly, the integrity of calcein-loaded Chol-rich liposomes was much lower than that of liposomes with low or no Chol during incubation with various strains of S. epidermidis. In vivo results in a zebrafish infection model (bacteremia) confirmed the superior activity of Chol-rich MOX-liposomes compared to the free drug.
Conclusion: The current in vitro and in vivo findings demonstrated the potential of PEGylated and Chol-rich liposomal antibiotics as highly efficient therapeutics for the treatment of S. epidermidis infections.
Keywords: Staphylococcus epidermidis; antibiotic; antimicrobial; cholesterol; in vivo; liposomes; moxifloxacin.
© 2025 Natsaridis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Moxifloxacin Liposomes: Effect of Liposome Preparation Method on Physicochemical Properties and Antimicrobial Activity against Staphylococcus epidermidis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 7;14(2):370. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020370. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214102 Free PMC article.
-
Encapsulation of vinorelbine into cholesterol-polyethylene glycol coated vesicles: drug loading and pharmacokinetic studies.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011 Mar;63(3):376-84. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.2010.01227.x. Epub 2011 Feb 8. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21749385
-
Impact of interfacial cholesterol-anchored polyethylene glycol on sterol-rich non-phospholipid liposomes.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014 Aug 15;428:111-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2014.04.031. Epub 2014 Apr 24. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014. PMID: 24910042
-
The interaction of phospholipid liposomes with bacteria and their use in the delivery of bactericides.J Drug Target. 1997;5(1):25-34. doi: 10.3109/10611869708995855. J Drug Target. 1997. PMID: 9524311
-
Liposomal drug delivery strategies to eradicate bacterial biofilms: Challenges, recent advances, and future perspectives.Int J Pharm. 2024 Apr 25;655:124046. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.124046. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38554739 Review.
References
-
- Antimisiaris SG. Introduction to liposome assisted drug delivery. In: Antimisiaris Sophia G., editor. Liposomes in Drug Delivery: What, Where, How and When to Deliver. Academic Press; 2024:1–17.
-
- Gkartziou F, Antimisiaris SG. Liposomes for infectious diseases. In: Antimisiaris Sophia G., editor. Liposomes in Drug Delivery: What, Where, How and When to Deliver (Academic Press; ). 2024:363–404.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

