The Predictive Significance of Various Prognostic Scoring Systems on the Efficacy of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40260026
- PMCID: PMC12010209
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.70713
The Predictive Significance of Various Prognostic Scoring Systems on the Efficacy of Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Background and aims: To evaluate the efficacy and prognostic value of various immunoprognostic scoring systems-Lung Immune Prognostic Index (LIPI), modified Glasgow Prognostic Score (mGPS), and Gustave Roussy Immune Score (GRIm)-in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs).
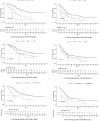
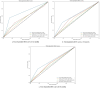
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of clinical data from 219 NSCLC patients treated with ICIs at Zhongshan Hospital (Xiamen), Fudan University from June 1, 2019 to January 31, 2024. The therapeutic efficacy and predictive capabilities of the scoring systems were assessed using Kaplan-Meier curves, Cox proportional hazards models, time-dependent ROC curves, and random survival forest models.
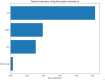
Results: The median follow-up was 29 months (IQR: 25.96-32.04), resulting in 93 observed deaths. Both LIPI and GRIm scores correlated with declining overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) as risk levels increased. LIPI demonstrated superior predictive performance at 12, 24, and 36 months (AUC: 0.70, 0.62, 0.61, respectively). Multivariate analysis identified immune-related adverse events (irAEs) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels as independent prognostic factors for OS.
Conclusion: LIPI serves as an effective prognostic tool for NSCLC patients receiving immunotherapy, outperforming individual inflammatory markers. Additionally, irAEs and LDH levels are significant independent prognostic factors for OS.
Keywords: Gustave Roussy Immune Score; Lung Immune Prognostic Index; immune checkpoint inhibitors; modified Glasgow Prognostic Score; non‐small cell lung cancer; prognostic analysis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Predictive Value of LIPI and iSEND Immune Scoring System in Immunotherapy of Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 20;25(11):803-810. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.102.47. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36419394 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Gustave Roussy Immune Score and Royal Marsden Hospital Prognostic Score Are Biomarkers of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitor for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.World J Oncol. 2019 Apr;10(2):90-100. doi: 10.14740/wjon1193. Epub 2019 Apr 20. World J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31068989 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Immunotherapy Outcomes in Older Patients with Solid Tumors Using the LIPI Score.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;14(20):5078. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205078. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291861 Free PMC article.
-
Prognosis stratification of cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors through lung immune prognostic index: a meta-analysis and systematic review.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 25;24(1):523. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12271-0. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38664760 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of the modified Glasgow Prognostic Score in NSCLC patients undergoing immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 11;14:1449853. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1449853. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39464717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang M., Herbst R. S., and Boshoff C., “Toward Personalized Treatment Approaches for Non‐Small‐Cell Lung Cancer,” Nature Medicine 27, no. 8 (2021): 1345–1356. - PubMed
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., et al., “Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 71, no. 3 (2021): 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Osmani L., Askin F., Gabrielson E., and Li Q. K., “Current WHO Guidelines and the Critical Role of Immunohistochemical Markers in the Subclassification of Non‐Small Cell Lung Carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving From Targeted Therapy to Immunotherapy,” Seminars in Cancer Biology 52 (2018): 103–109. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoy H., Lynch T., and Beck M., “Surgical Treatment of Lung Cancer,” Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America 31, no. 3 (2019): 303–313. - PubMed
-
- Reck M., Remon J., and Hellmann M. D., “First‐Line Immunotherapy for Non‐Small‐Cell Lung Cancer,” Journal of Clinical Oncology 40, no. 6 (2022): 586–597. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

