Antibody-Based Therapeutics in Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 40260055
- PMCID: PMC12009746
- DOI: 10.2147/BTT.S500460
Antibody-Based Therapeutics in Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Narrative Review
Abstract
Small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most aggressive lung cancer, mostly diagnosed at advanced stage, and with few therapeutic options for patients failing the first-line treatment. Antibody-based therapies, such as antibody-drug conjugates and T-cell engagers, are emerging as a promising option in the treatment of various solid tumors, including SCLC. T-cell engagers are molecules able to trigger the T-cell-mediated tumor cell death binding, at the same time, a T-cell and a tumor cell target. Tarlatamab is a DLL3-directed bi-specific T-cell engager (BiTE) whose efficacy was evaluated in a Phase 2 study. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) consist of a tumor-directed monoclonal antibody conjugated to a cytotoxic payload able to selectively kill tumor cells through different mechanisms. Ifinatamab-deruxtecan is an anti-B7-H3 ADC showing efficacy in pretreated SCLC patients in a phase 2 clinical trial. Sacituzumab govitecan is a Trop-2-directed ADC already used in other tumor types and evaluated in SCLC in the phase 2 TROPiCS-03 trial, with positive results. Bispecific antibodies targeting VEGF and PD-(L)1 showed antitumor activity in phase 1 and 2 clinical trials. Other antibody-based agents are currently at an earlier phase of their clinical development and showed a promising activity. Novel antibody-based agents could potentially acquire a prominent role in the treatment of SCLC, a field with few therapeutic options. Direct comparisons with the current standard of care still lack, however Phase 3 trials are currently ongoing.
Keywords: T-cell engager; antibody; antibody–drug conjugate; bispecific antibody; small-cell lung cancer; treatment.
© 2025 Torchia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Lorenza Landi received fees for membership of an advisory board or lectures from Pfizer, Novartis, AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, MSD, Lilly, Amgen, Sanofi, AbbVie, and J&J; Federico Cappuzzo received fees for membership of an advisory board or lectures from Roche, AstraZeneca, BMS, Pfizer, Takeda, Lilly, Bayer, Amgen, Sanofi, Pharmamar, Novocure, Mirati, Galecto, OSE, and MSD. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
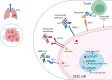
Figures
References
-
- Cohen S, Brennan B, Banerjee M, Kalemkerian GP. Temporal trends in small cell lung cancer: analysis of the U.S. surveillance, epidemiology and end results (SEER) database. JCO. 2023;41(16_suppl):e20641–e20641. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2023.41.16_suppl.e20641 - DOI
-
- Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019;394(10212):1929–1939. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

