Emerging regulators of gastric cancer angiogenesis: Synergistic effects of regulator of G protein signaling 4 and midkine
- PMID: 40260064
- PMCID: PMC12010818
- DOI: 10.25259/Cytojournal_212_2024
Emerging regulators of gastric cancer angiogenesis: Synergistic effects of regulator of G protein signaling 4 and midkine
Abstract
Objective: Globally, gastric cancer (GC) is among the most prevalent cancers. The development and spread of stomach cancer are significantly influenced by angiogenesis. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this process remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the role of the regulator of G protein signaling 4 (RGS4) in GC angiogenesis and its potential mechanisms.
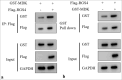
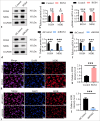
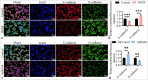
Material and methods: Through in vitro and in vivo experiments, including tube formation assays and xenograft models in nude mice, we evaluated the effects of RGS4 on GC angiogenesis and metastasis. In addition, we employed techniques such as immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence double staining to explore the interaction between RGS4 and midkine (MDK). Survival analysis was also performed to evaluate the association between the prognosis of patients with GC and the expression levels of RGS4 and MDK.
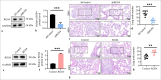
Results: Our findings revealed that RGS4 is a crucial factor in GC metastasis, significantly inducing angiogenesis. Further studies indicated that RGS4 directly interacts with MDK and upregulates its expression. By upregulating MDK, RGS4 stimulates the angiogenesis and metastasis of GC. Furthermore, a poor prognosis for patients with GC is directly linked to high expression of RGS4 and MDK.
Conclusion: This work is the first to clarify the molecular mechanism by which RGS4 upregulates MDK expression to increase GC angiogenesis. These findings not only enhance our understanding of the mechanisms underlying GC progression but also provide potential targets for developing new anti-angiogenic and antimetastatic therapies. RGS4 and MDK could serve as effective biomarkers for predicting the prognosis of patients with GC and offer new insights into personalized treatment approaches.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Midkine; Regulator of G protein signaling 4.
© 2025 The Author(s). Published by Scientific Scholar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
USP12 promotes breast cancer angiogenesis by maintaining midkine stability.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Nov 11;12(11):1074. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04102-y. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34759262 Free PMC article.
-
Midkine Is a Potential Therapeutic Target of Tumorigenesis, Angiogenesis, and Metastasis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 24;12(9):2402. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092402. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32847073 Free PMC article.
-
Midkine characterization in human ovaries: potential new variants in follicles.F S Sci. 2023 Nov;4(4):294-301. doi: 10.1016/j.xfss.2023.09.003. Epub 2023 Sep 20. F S Sci. 2023. PMID: 37739342
-
Shedding more light on the role of Midkine in hepatocellular carcinoma: New perspectives on diagnosis and therapy.IUBMB Life. 2021 Apr;73(4):659-669. doi: 10.1002/iub.2458. Epub 2021 Mar 3. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33625758 Review.
-
Midkine (MDK) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: More than a Biomarker.Cells. 2024 Jan 11;13(2):136. doi: 10.3390/cells13020136. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38247828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
