Elevational Synthetic Aperture Focusing for Rotated Array-Based Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging
- PMID: 40260101
- PMCID: PMC12011356
- DOI: 10.1109/access.2025.3549638
Elevational Synthetic Aperture Focusing for Rotated Array-Based Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Imaging
Abstract
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound (US) imaging is widely used for real-time, non-ionizing, and cost-effective medical diagnostics. However, using a one-dimensional (1D) transducer often results in limited elevational resolution due to the inherent beam thickness. In this paper, we introduce an elevational Synthetic Aperture Focusing (SAF) algorithm specifically designed for rotational 3D US imaging. Unlike previous methods requiring channel data, our approach operates on in-plane beamformed radio-frequency (RF) data, making it more accessible on many commercial scanners. Through simulations and experiments, we demonstrate significant improvements in elevational resolution (up to 96.4%) and contrast (up to 274.7%). These findings highlight the potential of the proposed algorithm to enhance both research and clinical applications of rotational 3D US imaging.
Keywords: Biomedical imaging; focusing; image processing; medical diagnostic imaging; ultrasonics imaging.
Figures


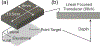

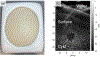








References
-
- Szabo TL, Diagnostic Ultrasound Imaging: Inside Out. New York, NY, USA: Academic, 2004.
-
- Smith SW, Lee W, Light ED, Yen JT, Wolf P, and Idriss S, “Two dimensional arrays for 3-D ultrasound imaging,” in Proc. IEEE Ultrason. Symp, vol. 2, May 2002, pp. 1545–1553.
-
- Light ED and Smith SW, “Two dimensional arrays for real time 3D intravascular ultrasound,” Ultrason. Imag, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 115–128, Apr. 2004. - PubMed
-
- Yen JT and Smith SW, “Real-time rectilinear 3-D ultrasound using receive mode multiplexing,” IEEE Trans. Ultrason., Ferroelectr., Freq. Control, vol. 51, no. 2, pp. 216–226, Feb. 2004. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
