Rod-Shaped NanoZnTPyP Paper-Based Sensor for Visual Detection of Dopamine in Human Plasma
- PMID: 40260265
- PMCID: PMC12011473
- DOI: 10.1155/jamc/9981628
Rod-Shaped NanoZnTPyP Paper-Based Sensor for Visual Detection of Dopamine in Human Plasma
Abstract
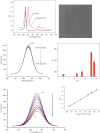
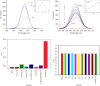
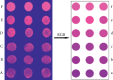
Dopamine (DA) is a catecholamine neurotransmitter secreted by the human adrenal medulla and is related to many medical diseases. The rapid and sensitive detection of DA levels in physiological media is attracting attention. This paper has developed a fluorescence paper-based sensor using CdTe quantum dots (QDs)-rod nanozinc 5, 10, 15, 20-tetra (4-pyridyl)-21H-23H-porphine (nanoZnTPyP) for sensitive and visual detection of DA. After adding DA, the original quenching fluorescence of the CdTe QDs-rod nanoZnTPyP sensor was effectively restored. The detection mechanism may be that the oxidation of DA to the alkaline CdTe QDs-rod nanoZnTPyP solution produced DA-quinine, and the recovery of fluorescence was caused by the electronic effect of DA-quinine and rod-shaped nanoZnTPyP. The detection range is 0.5∼10 nmol/L, and the limit of detection (LOD) is 0.38 nmol/L (S/N = 3). The sensor system was used on paper device to detect significant changes in the fluorescent color of DA at different concentrations. In addition, this method has been successfully used for the determination of DA in human plasma. The sensor system is simple, easy to operate, and has high selectivity for possible DA interfering substances, which provided new ideas for detecting DA and Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and other DA-related diseases.
Keywords: CdTe quantum dots; dopamine; fluorescence sensor; paper-based sensor; rod-shaped nanoZnTPyP.
Copyright © 2025 Linlin Yin et al. Journal of Analytical Methods in Chemistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A dual-potential electrochemiluminescence ratiometric sensor for sensitive detection of dopamine based on graphene-CdTe quantum dots and self-enhanced Ru(II) complex.Biosens Bioelectron. 2017 Apr 15;90:61-68. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.11.025. Epub 2016 Nov 11. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017. PMID: 27883960
-
Hollow structure molecularly imprinted ratiometric fluorescence sensor for the selective and sensitive detection of dopamine.Analyst. 2023 Jun 12;148(12):2844-2854. doi: 10.1039/d3an00528c. Analyst. 2023. PMID: 37232203
-
Fabrication of a Dopamine Sensor Based on Carboxyl Quantum Dots.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015 Oct;15(10):7871-5. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2015.11220. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26726431
-
A highly selective and simple fluorescent sensor for mercury (II) ion detection based on cysteamine-capped CdTe quantum dots synthesized by the reflux method.Luminescence. 2015 Jun;30(4):465-71. doi: 10.1002/bio.2761. Epub 2014 Sep 29. Luminescence. 2015. PMID: 25263990
-
Visual paper-based sensor for the highly sensitive detection of caffeine in food and biological matrix based on CdTe-nano ZnTPyP combined with chemometrics.Mikrochim Acta. 2021 Jan 6;188(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-04663-3. Mikrochim Acta. 2021. PMID: 33404824
References
-
- Saraji M., Shahvar A. Selective Micro Solid-Phase Extraction of Epinephrine, Norepinephrine and Dopamine from Human Urine and Plasma Using Aminophenylboronic Acid Covalently Immobilized on Magnetic Nanoparticles Followed by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Analytical Methods . 2016;8(4):830–839. doi: 10.1039/C5AY02036K. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

