Diagnostic accuracy of inter-eye difference of ganglion cell layer alone in identifying optic neuritis in multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 40260743
- PMCID: PMC12357966
- DOI: 10.1177/13524585251332895
Diagnostic accuracy of inter-eye difference of ganglion cell layer alone in identifying optic neuritis in multiple sclerosis
Abstract
Introduction: The 2024 McDonald criteria for diagnosing multiple sclerosis (MS) include optic nerve involvement as a fifth region for establishing dissemination in space. Optic neuritis (ON) can be detected through optical coherence tomography (OCT) using an inter-eye absolute or percentage difference (IEAD, IEPD) in ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) thickness.
Objective: To compare the diagnostic accuracy of GCIPL IEAD/IEPD with GCL and IPL IEAD/IEPD alone for identifying a history of ON.
Methods: This cross-sectional retrospective study included people with MS (pwMS) who underwent an OCT scan. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed using ROC analysis.
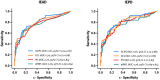
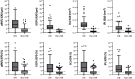
Results: A total of 241 pwMS (mean age 34.7 years [SD 9.7], 70.1% female) were included. Sixty-eight (28.2%) patients had a documented history of unilateral ON. GCL IEAD (AUC 0.79, cut-off ⩾ 0.06 mm3 or ⩾2µm, 58.9% sensitivity, 85.1% specificity) and IEPD (AUC 0.80, cut-off ⩾ 3%, 48.7% sensitivity, 89.8% specificity) demonstrated excellent diagnostic accuracy for unilateral ON, showing non-inferiority to the established GCIPL IEAD/IEPD.
Conclusion: GCL IEAD and IEPD provide strong diagnostic accuracy for identifying unilateral ON and can be effectively used as an alternative to GCIPL IEAD/IEPD to facilitate implementation in clinical routine.
Keywords: GCIPL; GCL; Multiple sclerosis; ganglion cell layer; ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer; inter-eye difference; optic neuritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: NK has participated in meetings sponsored by, received speaker honoraria or travel funding from Alexion, BMS/Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Merck, Novartis, Roche, and Sanofi-Genzyme and held a grant for a Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Training Fellowship Program from the European Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ECTRIMS). FF has participated in meetings sponsored by, received speaker honoraria or travel funding from Novartis. MP has participated in meetings sponsored by, received speaker or consulting honoraria or travel funding from Amicus, Merck, Novartis, and Sanofi-Genzyme. BK has received honoraria for speaking and for consulting from Biogen, BMS-Celgene, Johnson & Johnson, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Teva, and Sanofi-Genzyme outside of the submitted work. No conflict of interest with respect to the present study. FL has participated in meetings sponsored by, received speaker honoraria or travel funding from Actelion, Almirall, Biogen, Celgene, Johnson & Johnson, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva, and received honoraria for consulting Biogen, Celgene, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva. SM declares no conflict of interest relevant to this study. PR has received honoraria for consultancy/speaking from Alexion/Astra Zeneca, Allmiral, Amgen/Horizon, Amicus, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi has received research grants from Amicus, Biogen, Merck, Roche. CS declares no conflict of interest relevant to this study. KZ received speaking honoraria or travel grants from Biogen, Celgene/BMS, Novartis, and Sanofi-Genzyme. GZ has participated in meetings sponsored by or received travel funding from Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva. TZ has participated in meetings sponsored by or received travel funding from Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva. TB has participated in meetings sponsored by and received honoraria (lectures, advisory boards, consultations) from pharmaceutical companies marketing treatments for MS Allergan, Bayer, Biogen, Bionorica, BMS/Celgene, Genesis, GSK, GW/Jazz Pharma, Horizon, Janssen-Cilag, MedDay, Merck, Novartis, Octapharma, Roche, Sandoz, Sanofi-Genzyme, Teva, and UCB. His institution has received financial support in the past 12 months by unrestricted research grants (Biogen, Bayer, BMS/Celgene, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva and for participation in clinical trials in multiple sclerosis sponsored by Alexion, Bayer, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Octapharma, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva. BP has received honoraria for consulting from Novartis, has received honoraria for advisory boards/consulting from Chiesi and GenSight, and has received speaker honoraria from Novartis, Chiesi and Santen. GB has participated in meetings sponsored by, received speaker honoraria or travel funding from Biogen, Celgene/BMS, Lilly, MedWhizz, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva, and received honoraria for consulting Biogen, Celgene/BMS, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Genzyme, and Teva. He has received unrestricted research grants from Celgene/BMS and Novartis.
Figures

References
-
- Toosy AT, Mason DF, Miller DH. Optic neuritis. Lancet Neurol 2014; 13(1): 83–99. - PubMed
-
- Petzold A, Balcer LJ, Calabresi PA, et al. Retinal layer segmentation in multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2017; 16(10): 797–812. - PubMed
-
- Coric D, Balk LJ, Uitdehaag BMJ, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of optical coherence tomography inter-eye percentage difference for optic neuritis in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 2017; 24(12): 1479–1484. - PubMed
-
- Villoslada P, Sanchez-Dalmau B, Galetta S. Optical coherence tomography: A useful tool for identifying subclinical optic neuropathy in diagnosing multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2020; 95(6): 239–240. - PubMed
-
- Bsteh G, Hegen H, Altmann P, et al. Validation of inter-eye difference thresholds in optical coherence tomography for identification of optic neuritis in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler Relat Disord 2020; 45: 102403. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

