Glycine receptor activation promotes pancreatic islet cell proliferation via the PI3K/mTORC1/p70S6K pathway
- PMID: 40260914
- PMCID: PMC12016933
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.178754
Glycine receptor activation promotes pancreatic islet cell proliferation via the PI3K/mTORC1/p70S6K pathway
Abstract
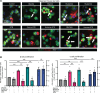
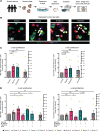
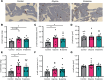
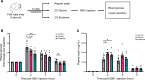
Glycine and β-alanine activate glycine receptors (GlyRs), with glycine known to enhance insulin secretion from pancreatic islet β cells, primarily through GlyR activation. However, the effects of GlyR activation on β cell proliferation have not been examined. Here, we aim to investigate the potential proliferative effects of glycine and β-alanine on islets. In vitro experiments on mouse and human islets revealed that glycine and β-alanine, via GlyR activation, stimulated the proliferation of β cells and α cells, without affecting insulin or glucagon secretion. Further analysis indicated the involvement of the PI3K/mTORC1/p70S6K signaling pathway in this process. Inhibition of GlyRs and PI3K/mTORC1/p70S6K signaling attenuated proliferative effects of glycine and β-alanine. In vivo and ex vivo studies supported these findings, showing increased β and α cell mass after 12 weeks of oral administration of glycine and β-alanine, with no changes in insulin secretion or glucose homeostasis under normal conditions. However, during an acute insulin resistance induced by insulin receptor antagonist S961, glycine and β-alanine enhanced insulin secretion and reduced blood glucose levels by increasing β cell secretory capacity. These findings demonstrate glycine and β-alanine in vivo and in vitro promote islet cell proliferation via GlyR activation and the PI3K/mTORC1/p70S6K pathway, potentially providing a target to enhance islet capacity.
Keywords: Beta cells; Diabetes; Endocrinology; Islet cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

